Work, Health and Safety Management System Manual
Disclaimer: This document contains material to assist in addressing Work Health and Safety management obligations. Every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of this information at the time of publication, it is provided as guidance only to current WHS legislation. This document contains material sourced from Safe Work Australia [1] and Work Safe QLD [2]. Any such material remains subject to copyright © to these governing bodies.
[1] https://www.safeworkaustralia.gov.au/copyright [2] https://www.worksafe.qld.gov.au/home/copyright
Introduction
This Work Health and Safety Management System (WHSMS) Manual is designed to assist in meeting Work Health and Safety (WHS) obligations under the current Work Health and Safety Act 2011 and current WHS Regulations 2011 and includes processes in place for management of health, safety and environment for Fabrication Lab workspaces located at The Edge State Library of Queensland. The WHSMS Manual will be available for inspection by all relevant persons, including visitors, direct relevant workers, contractors, Health and Safety Representatives (HSR), contractors, relevant workers of contractors and government appointed inspectors. Monitoring of the WHSMS Manual and updated as required and keep the most current copy at:
Hard Copy Location: The Edge Fabrication Lab, Clean Lab, Level 0, Staff office.
The WHSMS Manual will include essential information for people at the workspace to ensure health and safety as far as is reasonable. It will consist of roles and responsibilities of key personnel, Health and Safety Representative (HSR) and participation arrangements, guides for resolving issues, and processes in place for hazard identification, risk assessment and controls, managing incidents, emergency response and review/monitoring procedures.
Failure to comply with the requirements of the WHSMS Manual may lead to disciplinary action, which can include possible dismissal, loss of contract and legal action for severe breaches.
Note: For the purpose of this WHSMS, the term “workspace” includes any private, business or commercial premises/site, permanent or temporary, at any location, at which The Edge Fabrication Lab workers undertake related tasks/jobs, including the premises of the Person who Conducts a Business or Undertaking (PCBU).
Review Procedure
The Management will review the WHSMS Manual as required. The review schedule will be in response to organisational changes and relevant legislative amendments as they occur. Reviews will be undertaken in consultation with workers, HSR’s and other relevant parties. All relevant people will be made aware of changes made as a result of the review.
The WHSMS Manual will undertake review if:
- It is identified that there are changes in the workspace that affect the WHSMS;
- It is identified that the WHSMS is not effective;
- There are legislative changes that affect the WHSMS;
- There is a serious incident or dangerous occurrence or near miss.
The WHSMS Manual will be reviewed at least once (1) annually.
Document Control
The WHSMS Manual is a controlled document. All unauthorised copies either electronic or printed are considered uncontrolled copies. Copyholders and the version distributed to them will be recorded in the Distribution Record.
All versions of the WHSMS Manual will have a unique document number and version number, records of which kept in the Document Register, including the date of approval, and review date.
All versions of the WHSMS Manual are held as a record. In the event of a notifiable incident, the relevant WHSMS Manual and supporting documentation (initial and reviewed versions) will be held for a period of five years after the incident. During this period, the WHSMS Manual it will be accessible to all relevant persons and Government appointed officers as required.
Work Health and Safety Management System (WHSMS)
The State Library of Queensland recognises its moral and legal responsibility to provide a safe and healthy work environment for workers including contractors, volunteers, members and visitors to the space.
Objective: Our aim is to encourage a positive health and safety culture within the space. To ensure this occurs, work health and safety will be actively promoted throughout the organisation by the provision of information, training, instruction and supervision. The State Library will openly encourage all people to report hazards, including near misses, without fear of reprisal.
Scope: This applies to all people who are engaged to undertake tasks at The Edge Fabrication Lab workspaces/locations including workers, independent contractors and volunteers.
The State Library is committed to prevention of injury and ill health of its staff, contractors, volunteers, members and visitors within its working environment. It is to ensure that any work carried out within the scope of the business is conducted in compliance with the QLD Work Health and Safety Act 2011, QLD Work Health and Safety Regulation 2011 and complies with all applicable regulatory requirements.
Emphasis will be placed on effective management ensuring a systematic approach to the identification of risks using a hierarchy of controls and, the allocation of financial and physical resources to control these risks. In order to deliver these responsibilities, The State Library undertakes to:
- Maintain a safe and healthy space by providing plant, equipment and systems of work which reduces risks to people’s health and safety;
- Promote WHS awareness within the organisation and encourage workers to participate in the decision-making processes within the WHSMS;
- Ensure compliance with all relevant safety legislation, regulations, codes of practice and other requirements associated with our operations;
- Where any process or service is outsourced the State Library will determine criteria and methods of control to ensure conformity to our requirements and regulatory authorities.
- Arrange for the effective planning, organisation, control, monitoring and review of preventative and protective measures;
- Have in place a framework for setting and reviewing our WHS objectives and targets;
- Train, educate and inform our workers about WHS issues that may affect their work; and
- Commit to reporting WHS performance with measurable targets to ensure continued improvement.
This WHSMS is deemed appropriate for The Edge Fabrication Lab and includes a commitment to comply with the WHSMS and all applicable regulatory requirements.
Section 1 CONSULTATION, COOPERATION and COORDINATION
1.1 Consultation, Cooperation and Coordination
Objective: To establish formal consultation, cooperation and coordination methods, to allow workers and other duty holders, such as contractors and volunteers to address health and safety matters relevant to them.
Scope: This applies to all persons who conduct work for The Edge Fabrication Lab, irrespective of their individual employment arrangement. This covers all persons who are directed and/or engaged to undertake tasks at The Edge Fabrication Lab workspaces/locations including workers, independent contractors and volunteers. Also, visitors and any third parties that may be impacted by WHSMS at The Edge Fabrication Lab will be included in consultation and communication in respect of WHSMS matters as and when required, determined by the Workspace Manager/Supervisor/Health and Safety Representative.
The State Library will ensure formal Consultation, Cooperation and Coordination methods are established so workers and other duty holders, such as contractors and volunteers are aware of health and safety matters relevant to them. QLD WHS legislation requires a Person who Conducts a Business or Undertaking (PCBU) to consult with their workers and other relevant persons on matters that will or are likely to directly affect their health and safety. The State Library recognises the benefits that regular and effective consultation including, consultation, cooperation and coordination can produce and is committed to fulfilling this duty.
The State Library will follow AGREED consultative arrangements in line with WHS legislative requirements:
- Consult and work with SLQ health and safety committee;
- Elected a health and Safety Representative (HSR);
- Implement WHS as a standing agenda item at regular team meeting.
Further to this, consultation will take place in the following ways:
- Formal inductions;
- Training;
- Information on hazards and the existing WHSMS manual;
- Emergency response;
- Incident investigation and corrective actions;
- Results of WHSMS evaluations including audits, non-conformances;
- Review of WHSMS objectives;
- Safe work procedures;
- Risk assessments, risk controls and feedback regarding long-term controls;
- Safety Data Sheets (SDS), product safety sheets, operating manuals etc.;
- Reporting and keeping records in line with legislative requirements.
The State Library will modify the above information for languages other than English and those with learning disabilities as relevant/if needed.
The consultation will be timely and allow for relevant persons to contribute their views and feedback. Consider feedback on hazard identification, risk assessment and implementation of risk controls.
1.2 Consultation, Cooperation and Coordination Procedure
- Responsibilities:
At State library the management representative is responsible for ensuring that:
- There is an active consultation, cooperation and coordination procedure and associated mechanisms in place that meet legislative requirements;
- All workers are trained and familiar with, have access to and participate in the consultation, cooperation and coordination procedure and associated mechanisms while working at The Edge Fabrication Lab;
- All relevant workers and HSR are consulted in the preparation of Safe Operating Procedures (SOP);
- Others, who are impacted by WHSMS at The Edge Fabrication Lab, such as additional SLQ departments, contract workers, volunteers and visitors, are included in consultation as required;
- Review of the consultation, cooperation and coordination procedure as needed.
- Informing workers and others about the requirement to participate in activities, and follow, the consultation, cooperation and coordination procedure and associated mechanisms while working at The Edge Fabrication Lab;
- Ensuring there is adequate training for all people on how to consult and coordinate in the workspace;
- Conducting, and enabling, regular consultation with all workers and workgroups;
- Maintaining records relating to consultation.
The HSR/Safety Committee is responsible for:
- Maintaining and reviewing the consultation, cooperation and coordination procedure as required;
- Ensuring all workers have access to adequate consultation mechanisms and that they actively participate in consultation in the workspace;
- Informing and consulting with the Management Representative and CEO regarding consultation as necessary;
- Maintaining formal, approved consultation mechanisms and records required by legislation.
All workers and others are responsible for actively participating in consultation and for following reasonable directions in respect of WHSMS consultation procedures while working at The Edge Fabrication Lab.
- Procedure:
The State Library has established the following agreed consultative arrangements in line with WHS legislative requirements:
- Consult and work with SLQ health and Safety committee;
- Elected a Health and Safety Representative (HSR);
- Implement WHS as a standing agenda item at regular team meeting.
Consultation mechanisms at The Edge Fabrication Lab include the following:
- Formal induction training following the workspace induction procedure;
- Training as outlined in the training and competency assessment procedure and the workspace induction procedure;
- Information on hazards and the existing WHSMS Manual;
- Emergency response as described in the emergency management section of the WHSMS Manual;
- Incident investigation and corrective actions as detailed in the incident reporting procedure;
- Results of WHS evaluations including audits, non-conformances;
- Review of WHS objectives;
- Safe work procedures;
- Risk assessments, risk controls and feedback regarding long-term controls;
- SDS, product safety sheets, operating manuals etc.;
- Reporting and keeping records in line with legislative requirements.
In the first instance, workers who identify WHS issues in the workspace, or who wish to communicate with The Edge Fabrication Lab concerning WHS issues, should contact their supervisor or manager.
If it is not possible, or the worker feels uncomfortable to raise a particular WHS issue with their supervisor or the WHS manager, they should contact their HSR for assistance and consultation.
Workers who are HSR's are deemed to represent workers in particular work groups/departments and as such, will undertake regular, meaningful consultation with the workers in their work group. They will also respond to WHS issues raised with them by a worker or group of workers, by their duties as an HSR.
HSR's are then empowered to raise WHS issues formally at meetings with the supervisor or manager and with the Health and Safety Committee. They may in certain circumstances contact the relevant State authority for assistance and information.
The Health and Safety Committee will coordinate, manage, resolve and document any formally raised WHS issues, in consultation with the relevant workers and HSR's involved with the matter. They will then report and consult to the Management Representative and CEO regarding the nature and outcome of the issue.
The Management Representative will engage in the consultation procedure about WHS issues identified and raised at The Edge Fabrication Lab by the HSR or Health and Safety Committee.
The State Library will foster a culture of open communication and discussions relating to health and safety and furthermore, ensure that workers' interests are efficiently represented through formalised consultative arrangements.
The consultation will take place directly with workers, or where elected the HSR, to identify and assess hazards, before and during the implementation of risk controls, and whenever there are changes or new information. The consultation will be timely ensuring views are heard, and workers/duty holders can contribute to decision making as appropriate. In the event of a dispute about WHS issues, the issue resolution procedure will be followed.
The determination of the SLQ Health and Safety Committee is active to ensure all workers have ready access to an HSR (or Deputy HSR as agreed). The composition and location of work groups are as follows.
Health and Safety Representative
HSR’s and Deputy HSR’s will be elected via the following agreed procedures to represent the work groups for this workspace. The term of office of HSR’s/Deputy HSR’s may be up to 3 years and is open to re-election.
HSR Election Procedure
Workers may elect an HSR after agreement on work groups has been reached. The State library will provide any resources, facilities and assistance reasonably necessary to enable the elections to be conducted.
Undertake the following procedure:
- Call for nominees by inviting all work groups to participate:
- All workers are eligible to nominate and be elected as an HSR or deputy HSR for their defined work group;
- Workers will inform the Management Representative of the election date;
- Conduct election (either informally by a show of hands or a more formal process such as secret ballot):
- By the agreed method;
- Each member of the workgroup may only vote once in the election;
- Give all members of the workgroup the opportunity to vote;
- Advise workgroup members of the election results;
- Advise the Health and Safety Committee Chair of the election results.
Deputy HSR’s
In the HSR’s absence, a deputy HSR effectively becomes the HSR with the same powers of that role. Elect deputy HSRs in the same way as HSRs.
1.3 Safety Meetings
WHS meetings will be held Quarterly with the HSR and Management representative present. Any additional team members that are required to attend will be advised before the meeting date. The meeting is an opportunity to discuss improvement of operational practices and to develop safety plans.
Should the need arise for more frequent WHS meetings or an emergency debrief is required as a result of an incident, all relevant workers will be informed.
Safety Meeting Aims:
| * Making relevant workers’ more aware of safety at work; * Bringing together management and relevant workers; * Stimulating an interest in safety; * Educating relevant workers’ in safe working practices; * Accessing a more extensive range of viewpoints; * Developing preventive measures not reactive action; * Sharing incidents and workspace procedural changes. |
Records will be maintained of the topics covered; outcomes recorded, in the Safety Meeting/Safety Talk Record.
1.4 Issue Resolution
Objective: To ensure that all WHS issues arising in the workspace are resolved in an efficient, timely and suitable manner to enable maintenance of a safe and healthy work environment at The Edge Fabrication Lab.
Action: This will provide guidelines for a consultative, systematic and fair approach to resolving work health, safety or welfare issues that may arise. The Edge Fabrication Lab will adhere to the guidelines and requirements of the current QLD WHS Legislation and follows a process of natural justice to resolve any WHS issues raised in the workspace.
In attempting to resolve any WHS issue, The State Library will have regard to relevant matters, including, but not limited to:
- The degree and immediacy of the risk to workers or other people affected by the WHS issue;
- The number and location of workers and other people affected by the WHS issue;
- Corrective measures (temporary and permanent) that must be implemented to resolve the issue, using appropriate mechanisms to eliminate and control risks;
- Who will be responsible for implementing the resolution measures;
- Consultation between all parties involved and affected by the WHS issue.
Workers will not be penalised, in any way, due to a safety issue being raised and actioned at The Edge Fabrication Lab.
1.5 Issue Resolution Procedure
This procedure will provide a practical framework to enable the resolution of any WHS issue that may arise at The Edge Fabrication Lab.
- Responsibilities:
At the State library the Management Representative is responsible for ensuring that:
- There is an effective Issue Resolution Procedure and associated mechanisms in place that meet legislative requirements;
- All The Edge Fabrication Lab workers, when required, are trained and familiar with, have access to and participate in the Issue Resolution Procedure and related devices;
- Conduct a review of the Issue Resolution Procedure as required.
- Informing workers and others about the requirement to participate, and follow, the Issue Resolution Procedure and associated mechanisms while working at The Edge Fabrication Lab;
- Ensuring adequate training for all relevant workers on how to track and action the Issue Resolution Procedure in the workspace;
- Conducting, and enabling, issue resolution when required with all workers and workgroups;
- Maintaining records required by legislation relating to issue resolution.
The HSR/Health and Safety Committee is responsible for:
- Maintaining and reviewing the Issue Resolution Procedure as required;
- Ensuring all workers have access to adequate issue resolution information and mechanisms and that they actively participate in issue resolution when needed in the workspace;
- Informing and consulting with the Management Representative/CEO regarding issue resolution as necessary;
- Maintaining formal, approved issue resolution mechanisms and records required by legislation;
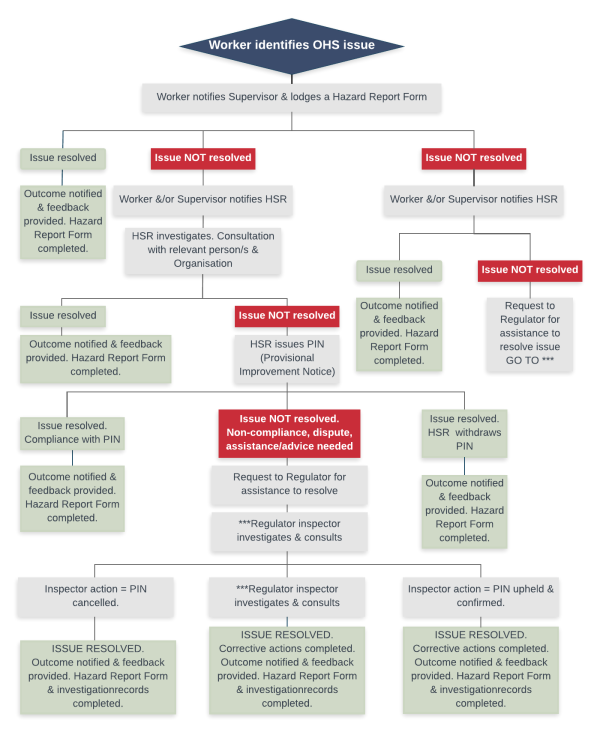
- Seeking assistance from the regulator when needed, as per the Issue Resolution Procedure Flow Chart (Figure1. page 12) and the requirements of current legislation.
All workers are responsible for actively participating in and following reasonable directions in respect of issue resolution while working at The Edge Fabrication Lab when required.
Figure1. Issue Resolution Procedure Flow Chart
Informal Issue Resolution Procedure: A workers who wishes to raise a WHS hazard/concern should first discuss the issue directly with their supervisor or manager. The supervisor/manager will:
- Consider and investigate the matter, including contacting other relevant workers at The Edge Fabrication Lab who may be able to assist in resolving the WHS issue;
- If possible, implement or arrange to implement, actions to address the hazard/issue, as soon as possible;
- Consult with and inform the worker who raised the issue of the outcome of the investigation, and all corrective actions;
- Ensure to complete and retain a Hazard Report Form as a record of the issue, the result and resolution;
- Monitor and review the issue at an appropriate and agreed time to ensure there is no repeat of the issue.
If the WHS issue is resolved satisfactorily at this stage, then there is no need for further action.
If the WHS issue is NOT resolved, at this stage, the problem will progress to the Formal Issue Resolution Procedure. Refer to Figure 1. Issue Resolution Procedure - Flow Chart.
In the event of a severe immediate risk to workers: In the situation when a definite and direct safety hazard is perceived, and the issue is considered critical and urgent, the worker or HSR will inform the relevant supervisor, who will call an immediate halt to work to investigate the matter.
If the Management Representative fails to agree about the degree of risk present or is not available, an HSR or a worker from that workgroup will direct affected workers (and any others who may be affected) to withdraw from the alleged hazard. They will then inform the appropriate manager of the actions taken pending a full investigation.
Work will not resume until the hazard has been controlled and no longer presents an unacceptable risk to the safety and health of workers and others.
Section 2 RISK MANAGEMENT
2.1 Risk Management
Objective: To embed principles of effective risk management into existing practices at all levels of the organisation.
Scope: This applies to all workers of the State Library, irrespective of their employment arrangement. This covers all people engaged to undertake tasks at The Edge Fabrication Lab workspaces/locations including independent contractors and volunteers.
Action: Risk is inherent in all The Edge Fabrication Lab functions. All The Edge Fabrication Lab personnel are responsible for managing the risks that relate to their particular area of work.
The following structure for risk management will apply.
- Where specific regulations require certain controls:
- The Edge Fabrication Lab will ensure compliance with those matters, in consultation with relevant persons (including Duty Holders/Contractors);
- Hazard Identification:
- Identify reasonably foreseeable hazards that may pose risks to health and safety;
- Evaluate risks where required:
- Compare estimated levels of risk against pre-established criteria (including a risk matrix) and consider the balance between potential benefits and adverse outcomes;
- Manage risk:
- Elimination of risk being the first option investigated and instigated for a control action;
- Where the risk cannot be eliminated, minimise the risk so far as is reasonably practicable;
- Implement risk controls:
- Secondary to elimination, selection of controls will follow a hierarchy:
- Substitution with less hazardous options;
- Isolate people from the hazards;
- Use of engineering controls;
- Where risk remains:
- Implement administrative controls;
- Where risk remains:
- Use of PPE;
- Use any one or a combination of these controls as appropriate;
- All controls must be fit for purpose, suitable for the nature and duration of task and installed set-up, and used correctly;
- Review risk controls whenever:
- Control is no longer effective;
- Before any change likely to introduce new or different hazards that current controls will not adequately address;
- A further hazard or risk is identified;
- Results of consultation indicate a review is needed where requested by workers or Health and Safety Representative.
2.2 Risk Management Procedure
This procedure will assist in the early detection of hazards, the assessment of risks and the implementation of control mechanisms in line with the needs of the workspace.
- Responsibilities:
At The Edge Fabrication Lab the Management Representative is responsible for ensuring that:
- There is an effective Risk Management Procedure and associated mechanisms in place and that they meet QLD WHS and Worker’s Compensation legislative requirements;
- All workers are trained and familiar with, have access to, and participate in risk management policies, procedures and activities while working at The Edge Fabrication Lab;
- Others who are impacted by WHS at The Edge Fabrication Lab, such as additional SLQ departments, volunteers and visitors, are included in risk management strategies as required;
- Conduct a review of the Risk Management Procedure as necessary.
- Informing workers and others about the requirement to actively participate in risk management strategies and to follow risk management policies and procedures while working at The Edge Fabrication Lab;
- Ensuring adequate training for all people in how to participate in risk management activities in the workspace;
- Maintaining records required by current QLD WHS Legislation relating to risk management.
All workers are responsible for working safely and for following reasonable directions in respect of the WHS Risk Management Procedure and associated mechanisms while working at The Edge Fabrication Lab.
- Procedure:
The State Library has implemented a step-by-step mechanism to provide the required system and tools to ensure effective risk management in the workspace. They are as follows:
- Communication – the Consultation, Cooperation and Coordination and associated procedure are in place to enable risk management to be implemented systematically and efficiently, involving all people impacted by WHS at The Edge Fabrication Lab. Effective consultation and planning is essential during every phase of the Risk Management Procedure and associated activities;
- Hazards are identified and reported via the following:
- Consultation – WHS Meetings, HSR, briefings, direct discussions etc.;
- Workspace inspections;
- Audits – internal and external (photos, observations, checklists, reports);
- Reporting – Incident Forms, Hazard Report Form, Hazardous Chemicals/Dangerous Goods Register etc.;
- Research – gather and interpret information from State and Local Authorities, manufacturers, suppliers, industry groups, other PCBU and workers;
- Risk assessment – conduct workspace-specific, task-specific, chemical and plant risk assessments and environmental impact risk assessments as required by suitably trained and experienced workers;
- A Risk Assessment Matrix (figure 2) which accompanies each risk assessment form is used to assist in determining risk levels;
- Actions prioritised – assess risk levels then a list of action priorities is determined;
- Risk control – identified hazards are systematically eliminated or reduced by implementing practical control measures. Use the Hierarchy of Controls (Figure 3);
- Monitor and review – regular checks are carried out to ensure the implementation of suitable control measures, that they continue to be adequate, and that no new hazards have been introduced into the workspace either by implemented control actions or by changes to the workspace;
- Documentation – all risk management activities conducted and the outcome of those activities, in particular, those outlined in this procedure, are fully documented and records maintained.
It is essential that workers continue to look for hazards in the workspace at all times, not just during risk management activities. All hazards that cannot be eliminated immediately must be reported to the Management Representative using hazard-reporting mechanisms. Consider the potential for the introduction of new hazards in the workspace when planning or changing work tasks, equipment etc. in the workspace.
Environmental risk management, including the potential for chemical spillage, is included in all relevant risk management policies and procedures within The Edge Fabrication Lab.
Where identified hazards and risks are well known and subjected to accepted risk control measures, no further risk assessment will be required, and risk controls can be implemented. These controls, however, will be monitored and reviewed accordingly. For all other identified hazards, a risk assessment or job safety analysis must be undertaken to determine how likely to the hazard is to harm people, and how severe the harm could be. The process used to conduct a risk assessment is outlined below in Figure 2 Risk Assessment Matrix.
Risk Assessment Matrix
| Stage 1: Determine Likelihood: What is the possibility that the effect will occur? | ||
|---|---|---|
| Likelihood | Criteria | Description |
| Almost certain | Expected in most circumstances. | The effect is a typical result. |
| Likely | Will probably occur in most circumstances. | The effect is known to have occurred previously. |
| Possible | Might occur at some time. | The effect could occur or, examples of it happening. |
| Unlikely | Could occur at some time. | The effect is not likely to occur or, no examples of it happening before. |
| Rare | May occur only in exceptional circumstances. | The effect is practically impossible. |
| Stage 2: Determine Consequence: What will be the expected effect? | |
|---|---|
| Level of Effect: | E.G. of each level: |
| Insignificant/Acceptable | No effect or treatment required - or so minor that effect is acceptable. |
| Minor | Minor effect or injury - On-site first aid treatment only. |
| Moderate | Serious injuries - Injury requiring medical treatment. |
| Major | Extensive injury - Requires specialist medical treatment or hospitalisation. |
| Catastrophic | Permanent total disability injury, multiple injuries and death/es. Substantial environmental harm, prosecution/imprisonment. |
| Stage 3: Determine the risk score: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consequence | |||||
| Likelihood | Insignificant | Minor | Moderate | Major | Catastrophic |
| Almost certain | 3 High | 3 High | 4 Extreme | 4 Extreme | 4 Extreme |
| Likely | 2 Mod. | 3 High | 3 High | 4 Extreme | 4 Extreme |
| Possible | 1 Low | 2 Mod. | 3 High | 4 Extreme | 4 Extreme |
| Unlikely | 1 Low | 1 Low | 2 Mod. | 3 High | 4 Extreme |
| Rare | 1 Low | 1 Low | 2 Mod. | 3 High | 3 High |
| Stage 4: Record risk score on the worksheet: (Note – Risk scores have no absolute value and should only be used for comparison and to engender discussion.) | |
|---|---|
| Score | Action |
| 4E: Extreme | DO NOT PROCEED. Requires immediate attention. Introduce further high-level controls to lower the risk level. Re-assess before proceeding. |
| 3H: High | Review before commencing work. Introduce new controls and/or maintain high-level controls to lower the risk level. Monitor frequently to ensure control measures are working. |
| 2M: Mod. | Maintain control measures. Proceed with work. Monitor and review regularly, and if any equipment/people/materials/work processes or procedures change. |
| 1L: Low | Record and monitor. Proceed with work. Review regularly, and if any equipment/people/materials/work processes or procedures change. |
Figure 2. Risk Assessment Matrix
Work health and safety laws require selecting risk controls following a “Hierarchy of Control”. As far as reasonably practical, risk must be eliminated. Where this is not possible, risk can be reduced using substitution, isolation and engineering controls. For remaining risk, use administrative controls and PPE. Risk controls must be reviewed and monitored to ensure they remain effective.
All controls will be reviewed and monitored:
| * When/if incident/near miss occurs; * As per legislative requirements; | * As requested by relevant persons (such as HSR); * Other times necessary to ensure effectiveness. |
It is essential to consult with relevant workers during the selection of controls and remember that any changes to the task (including introducing new equipment and ways of doing things) can result in further risks. Provide sufficient training, information, instruction and supervision where required.
| Elimination - Risk will be eliminated where possible. Examples: | ||
|---|---|---|
| No Hazardous Manual Handling tasks | No hot work | Pre-cut and pre-made materials / parts |
| Substitution Isolation Engineering - Where risk remains, one/combination of controls will be used. Examples: | ||
| * Store and stack items to minimise risk from hazardous manual handling * Restrict weight and size of items to be handled manually * Industrial racking systems * Use mechanical lifting and materials handling devices | * Welding bay * Welding curtains * Gas bottle trolleys * Restricted zones in workshop * No chemicals or flammable materials in or near hot work area | * Guards on machines/tools to prevent access to blades, pinch spots, moving parts * E- stops, Lock Out and Tag * Operator bays/restricted zones * Sensor curtains / alarms |
| Administrative - Where risk remains, administrative controls will be used. Examples: | ||
| * Risk Assessment * Hazardous Manual Task training | * Operational manuals * Hot Work Permits * Signage | * Training and education * Machine/vehicle maintenance programs * Pre-start checklists |
| Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) - Where risk still remains, it will be reduced as far as reasonably practicable with use of PPE. Examples | ||
| * High visibility vest * Gloves * Overalls | * Full face shield * Hearing protection * Welders Gloves | * Welding apron * Safety goggles/glasses * Work boots |
Figure 3. Hierarchy of Controls
2.3 Objectives and Targets
Objective: To provide all State Library workers and others with achievable, measurable and accountable outcomes.
Scope: These objectives and targets apply at all The Edge Fabrication Lab workspaces and will fall under the responsibility of nominated managers/supervisors.
The State Library is dedicated to providing a workspace that is free of injury and illness and promotes a culture of safety first. The Edge Fabrication Lab is committed to making WHS an integral part of decision making in all operations.
The State Library will measure objectives based on the following:
- Having a WHSMS that incorporates both WHS outcomes measurements and positive performance of risk management processes;
- The provision of physical and human resources to ensure that the objectives and targets of all WHS policies and procedures embedded within the WHSMS Manual will be achieved;
- Meet WHS Legislative requirements;
- An open and transparent consultation that encourages and enables continual improvement of internal systems and outcomes.
Targets will include:
- Reduction in Lost Time Injury (LTI) rate annually; (Human Resources)
- Reduction in LTI – average days lost; (Human Resources)
- Complete inspections/audits within specified timeframes; (WHS Committee)
- Corrective actions completed within specified timeframes; (WHS Committee/HSR)
- Undertake Emergency Response Plan practices within specified timeframes; (WHSA)
- Review of consultative arrangements. (WHS Committee)
Performance targets will be set specific to the workspace and incorporated into position descriptions and performance evaluation for individuals and organisation.
2.4 Objectives and Targets Procedure
WHS performance in the workspace will be measured and analysed and responsibilities allocated to individuals within the company to assist in meeting WHS targets and to encourage continual improvement.
- Responsibilities:
At The Edge Fabrication Lab the Management Representative is responsible for ensuring that they:
- Develop and implement a WHSMS Manual;
- Identify and assess the training needs of workers;
- Establish contractor management procedures;
- Establish effective consultation mechanisms with all relevant persons.
- Assist with the implementation and day to day operation of the WHSMS Manual;
- Provide and organise WHSMS training for workers as required;
- Respond quickly to hazards reports and action corrective actions;
- Respond to incidents and ensure procedures are followed and undertake investigations as appropriate;
- Ensure implementation, monitoring and reviews of contractor management procedures;
- Practically implement consultation mechanisms with workers, contractors, volunteers and other departments.
Workers are responsible to:
- Know and follow the WHSMS Manual and WHSMS plans at The Edge Fabrication Lab;
- Participate in WHS training and induction as and when required;
- Participate in return to work plans;
- Cooperate with incident investigations and hazard corrective actions;
- Actively participate in consultation in the workspace.
- Procedure
Objectives:
- All workers are informed and trained in their WHS roles and responsibilities;
- All workers conduct themselves in a safe and responsible manner;
- Identify and meet WHS training needs;
- Minimise incident frequency and severity;
- Contractor management systems are in place and working effectively;
- WHSMS is in place and implemented effectively by all workers and management;
- Undertake workspace inspections and audits;
- Hazards are identified, and action is taken to eliminate or reduce and control related risk;
- To fully document all WHSMS activities, training, incidents, systems and outcomes in the workspace.
Targets:
- All workers know and adhere to their WHS roles and responsibilities;
- All workers are familiar with and follow the WHSMS;
- All workers are trained and deemed competent in accordance with the requirements of their job and current WHS Legislation;
- Zero incidents and injuries;
- Contractors produce evidence of insurances, SOP and demonstrate knowledge and competency in safe work practices and WHS systems;
- The WHSMS is fully implemented and operating effectively at The Edge Fabrication Lab;
- Workspace inspections and audits are conducted at least annually and more frequently as required;
- Documented records are kept of all WHS matters, incidents, training, inspections, and audits as required by current WHS Legislation.
Roles, Responsibilities and Accountabilities
Objective: Everyone in the workspace understands the need for health and safety, what their role is in making the workspace safer, and how they can fulfil their responsibilities and duties.
Scope: This applies to all workers, contractors and volunteers of The Edge Fabrication Lab.
Successfully managing health and safety in the workspace and environmental protection relies on commitment, consultation and co-operation.
The Edge Fabrication Lab allocates the following roles and responsibilities:
State Librarian/CEO (Officer):
- Approval of WHSMS documentation;
- Communication of WHSMS policies and objectives;
- WHSMS leadership;
- Allocating sufficient WHSMS resources;
- Reviewing WHS performance;
- Providing direction for increasing WHS performance;
- Establishing and promoting a WHS culture;
- Legal obligations to provide and maintain a safe workspace.
Applied Creativity Lead (Management):
| * Integration of WHS into all decision making; * Consult with workers and other duty holders/contractors; * Plan, develop, implement, monitor and review WHSMS policies, procedures and plans; * Control risks; * Support WHS committees; * Provide WHS communication; * Discuss WHS at relevant meetings; * Identify WHS training needs and enable training as required; * Reporting and recording; * Liaise with relevant regulatory authorities; * Legal obligations to provide and maintain a safe workspace. |
WHS Committees:
| * Develop, monitor and review WHSMS policies and procedures; * Monitor and report on WHS performance; * Monitor changes in legislation; * Review corrective actions; * Provide WHS information to workers. |
All workers, contractors and volunteers:
- Comply with WHS policies, procedures and plans;
- Work in a manner that is safe and does not create risks for themselves or others;
- Report and assist in rectifying hazards;
- Participate in consultative arrangements;
- Legal obligations to not endanger others by their acts or omissions.
| Roles, Responsibilities and Accountabilities Procedure | ||
| State Librarian/CEO | > | * Provision and maintenance of a work environment that is safe and without risks as far as is reasonably practicable; * Approve WHSMS; * Accountable for breaches of current WHS Legislation. |
| v | ||
| Applied Creativity Management | > | * Provision and maintenance of a work environment that is safe and without risks as far as is reasonably practicable; * Oversee WHSMS and consult with relevant persons; * Accountable for breaches of current WHS Legislation; * Integration of health and safety into all aspects of decision-making and operations; * Meeting WHS targets and objectives; * Monitoring, assessing and reviewing work health and safety. * Development and implementation of WHSMS, Monitoring, assessing and reviewing work health and safety targets and objectives; * Training and consultation; * Supporting and assisting workers with post-injury management. |
| v | ||
| WHSA SLQ WHS Committee | > | * Monitoring, assessing and reviewing WHSMS, SOP and WHS targets and objectives. * Meet as per agreed “Charter” to discuss WHS matters relating to The Edge Fabrication Lab including incidents, corrective actions and areas for improvement/target areas; |
| v | ||
| The Edge Fabrication Lab Workers Contractors Volunteers | > | * Take reasonable care of themselves and others at in the workspace; * Cooperate with WHS policies and procedures and relevant legislation/guidance; * Participation in consultative arrangements regarding WHS matters; * Assisting management to meet WHS targets and objectives. |
2.7 Environmental Management
Objective: To actively work towards elimination and reduction of adverse effects to the environment by incorporating environmental impacts into all levels of the organisation and utilising best practice techniques wherever possible. To work with workers, visitors and business partners to achieve compatibility between economic development and the maintenance of the environment to minimise harm.
The State Library recognises its moral and legal responsibility to minimise damage to the environment caused by work activities and is committed to conducting our business in an environmentally aware and responsible manner.
This commitment extends to ensuring that operations do not unnecessarily endanger flora, fauna, sensitive areas, workspaces of heritage importance or present concerns to members of the public and community.
The Edge Fabrication Lab will endeavour to minimise the impact of the following:
- Atmospheric emissions;
- Workspace contamination and spills;
- Noise emission;
- Damage to flora and fauna;
- Damage to, or interference with workspaces, areas or structures of indigenous or non-indigenous cultural heritage;
- Storm water management;
- Unnecessary energy consumption.
To fulfil this commitment, the State Library, will observe all environmental laws and promote environmental awareness among all workers to increase understanding of environmental matters.
The State Library will actively take part in the following:
- Assess eco-footprint to identify environmental impacts and move towards more sustainable practices;
- Identify waste streams and options for effective waste management;
- Improve purchasing (buy recycled materials, reduce waste, use less harmful/volatile chemicals and energy efficient equipment/appliances);
- Monitor energy consumption and promote equipment/appliance shut down during non-operational periods.
- Improve storage (minimise quantity, waste and spills, reduce odours by keeping containers closed);
- Conserve water (install water-saving accessories, repair leaks);
- Preserve waterways (clearly mark and protect stormwater drains);
- Emergency planning and spill response;
- Seek appropriate licenses/permits from State Environmental Protection Agencies and other relevant authorities;
- Notify relevant authority in the event of a significant environmental impact.
Section 3 MONITORING and REVIEWING
3.1 Legislative Change
Objective: Maintain awareness of legislative change.
Scope: This applies to all workers of the State Library charged with the responsibility to identify, monitor and action compliance as per legislation relevant to work health and safety of workers.
The State Library is committed to providing a safe and healthy workspace for workers, contractors and visitors and embraces opportunities to improve knowledge about new legislation and best practice solutions.
The State Library will proactively seek out advice, education and industry knowledge to foster continual improvement in WHS systems and updates of relevant legislation.
The State Library will endeavour to manage legislative change by:
- Assigning responsibilities for researching legislative variations with State and Federal Authorities;
- Participating in learning opportunities such as information sessions provided by industry stakeholder groups, unions, and relevant authorities;
- Seeking advice from suitably qualified people where required (such as work consultants);
- Attending conferences, trade shows etc. where possible;
- Ensuring refresher training is undertaken where required;
- Liaising with local authorities as needed.
3.2 Legislative Change Procedure
- Procedure:
The State Library has put in place mechanisms to manage legislative change by delegating the Work, Health and Safety Advisor WHSA to:
- Regularly reviewing WHS policies, procedures, systems and processes to ensure they are current and in line with relevant legislation;
- Reviewing WHSMS policies, procedures, systems and processes to maintain currency;
- Notifying, all relevant persons on the changes;
- Maintaining documented records of modifications to policies, procedures, systems and methods due to legislative changes via the document control system. Seeking advice from suitably qualified persons where required (such as WHS consultants) to assist with management of legislative changes;
- Ensuring workers can access relevant WHS information either in electronic form or hard copies as required;
- Liaising with local authorities as required.
3.3 Management Review
Objective: To identify areas for improvement in the management of the WHSMS.
Scope: This applies to all the State Library workers who sit on a WHS Committee, are an HSR or are a relevant managers/supervisor responsible for planning, development, use, and maintenance of the WHSMS.
The State Library recognises the importance of reviewing the adequacy and effectiveness of the WHSMS to identify opportunities for improvement.
Management meetings will be held at regular intervals and will include the following agenda items:
| * Review of internal and external audit results, inspection and other compliance plans; * Evaluation of legal compliance issues; * Results of participation and consultation from all levels - management, workers and contractors; * Performance evaluation of the WHSMS Manual and objectives; * Status of incident reports, investigations, corrective and preventive actions; * Communication from interested parties, complaints - take action status and suggestions; * Management of change; * Corrective actions, accountability and timeframes; * Follow-up action on previous management reviews. |
Determine meeting intervals/timeframes on a risk basis. Meeting minutes will be recorded, and results of these will be provided to Senior Management/Directors/Board Members.
3.4 Management Review Procedure
This procedure is accessible to all State Library workers, and all workers can input into the WHS management review process via management or elected HSR.
WHS Committee are held at regular intervals and include the following management review agenda items:
- Legislative requirements - including incident notification, hazardous work, licensing, certification and audits;
- Review of internal and external audit results, inspection and other compliance plans;
- Evaluation of legal compliance issues;
- Results of participation and consultation from all levels - management, workers and contractors;
- Performance evaluation of the WHSMS and objectives;
- Status of incident reports, investigations, corrective and preventive actions;
- Hazard reporting - corrective actions, accountability and timeframes;
- Recommendations for continual improvement;
- Communication between workers and other relevant parties, complaints - take action status and suggestions;
- Planned changes to the WHS (documents, processes, training etc.) that affect workers;
- Management of legislative change;
3.5 Compliance Evaluation
Objective: To establish an annual audit plan to identify any areas for improvement.
Scope: This applies to all State Library workers.
The Management Representative will evaluate performance and compliance with the current WHS Legislation and the worker's compensation provisions to create benchmarks for continual improvement of workspace safety.
The State Library is committed to the continual development, improvement and implementation of its work health and safety management systems.
At the State Library, compliance with legislation and this WHSMS is evaluated using several strategies including, but not limited to:
- Review of internal and external audit results, inspection and other compliance plans;
- Evaluation of legal compliance issues;
- Results of consultation from all levels - management, workers and contractors;
- Performance evaluation of the WHSMS Manual and work, health and safety objectives;
- Status of incident reports, investigations, corrective and preventive actions;
- Communication from interested parties, complaints - take action status and suggestions;
- Corrective actions, accountability and timeframes;
- Follow-up on previous compliance reviews.
3.6 Compliance Evaluation Procedure
The State Library will implement the following:
- In-house inspections as required:
- Routine maintenance plans;
- Internal audits;
- External audits as required;
- Health surveillance monitoring where needed;
- Resourcing for inspections by regulatory bodies.
Undertake audits to evaluate compliance in line with:
- Legal obligations;
- Current WHSM Act and current WHS Regulations;
- The Edge Fabrication Lab WHSMS policies and procedures;
- AS/NZS 4801: 2001 Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems.
Reports detailing compliance evaluations, including audit and workspace inspection results will be recorded and results provided to SLQ WHS Committee or State Librarian/CEO at regular intervals.
Results of any audits, inspections and any corrective actions that indicate workers and relevant contractors may be at immediate at risk of harm must be actioned immediately.
3.7 Internal Audits
Objective: To define the process for undertaking internal audits of the defined WHSMS. This process will define the responsibilities for planning and conducting audits, reporting the results of audits, and retention of audit records.
The State Library is committed to assessing compliance with the WHSMS. By doing so we are ensuring that the system itself is effectively implemented and maintained. In order to assess compliance, regular internal audits will be undertaken.
Audit plans identifying criteria, scope, frequency, and methods will be developed and administered by the WHSA (or delegate). Audits will be scheduled, organised, performed and recorded in accordance with detailed procedures and work instructions. Suitably competent persons who are not accountable for WHS outcomes in the area being audited will perform audits.
All audit findings and results will be maintained and where corrective actions are identified, a report created accordingly, and management responsible for the non-conforming result ensure the necessary correction actions are taken without undue delay. All follow-up actions will be verified and signed off as complete by the WHS Manager (or delegate).
- Audit Procedure
Management Representative is required to:
- Implement an Audit Schedule to determine whether the WHSMS conforms to the documented policies and procedures;
- Allocate sufficient resources to ensure the WHSMS is properly effected and maintained;
- Provide audit findings to SLQ WHS Committee, WHSA, State librarian/CEO;
- Conduct all audits in a professional manner.
All Workers are required to:
- Participate and assist in internal audits as required;
- Bring it to the attention of their supervisor/manager immediately any issue that may affect a current audit.
The Management Representative will:
- Develop an internal audit plan;
- Ensure an internal audit of the WHSMS is undertaken annually (At minimum);
- Select an audit team (ensuring the auditor team has appropriate audit training);
- Appoint an leader auditor (if not themselves);
- Establish and implement an Internal Audit Plan; (considering breadth and depth of audit);
- Communicate the audit schedule to the organisation;
Audit Team Selection:
One or more auditors may comprise an audit team:
- If the team is made up of more than one auditor, a Lead Auditor will be nominated;
- The Lead Auditor will be responsible for coordinating the audit process, and preparation of the final audit report;
- The Lead Auditor will ensure that the team understands the scope of the audit;
- The Lead Auditor will ensure that relevant organisational WHSMS policies, procedures and other documents are made available before the audit commences (ensuring a reasonable notification time for audited departments prior to the audit).
- Audit Plan
The Lead Auditor is responsible for ensuring the preparation of a written audit plan. See Fabrication Lab Inspection Checklist.
The audit plan will consider:
- Relevant system documents and records;
- Internal audit criteria and components
Conducting the Audit:
- A pre-audit meeting is held with appropriate personnel to confer on the scope, plan and timing for the audit;
- The Lead Auditor may modify the audit scope and plan if necessary;
- All audit findings must be documented;
- Corrective actions from previous audits must be considered and documented;
- A post-audit meeting will be held to present preliminary audit findings, clarify any misinterpretations, and summarise the audit outcomes.
Reporting audit outcomes:
- The Lead Auditor will prepare an audit report;
- The audit report will state the scope of the audit, identify the audit team, define the evidence used, and summarise the results of the audit;
- Audit findings indicating that corrective actions are required must be entered into the Corrective / Preventative Action Register;
- The Management Representative is responsible for distributing the audit results to SLQ Work, Health and Safety Advisors WHSA, WHS Committee, State Librarian/CEO
The Management is responsible to ensure audit reports are tabled for review at next Management Review (see next section).
Audit follow-up:
- Non-conformances identified as a result of the audit will be listed in the Corrective / Preventative Action Register;
- The Management Representative will be responsible for the completion and effectiveness of corrective actions.
Record keeping:
- All Internal Audit Reports will be retained for at least two years from the date of the Audit;
- The WHS System Audit manager is responsible for assigning audit records to the WHS System Manager for storage (including any records relating to the training of auditors).
Note: Should any evidence collected during the internal audit suggest an extreme risk exists, this information must be communicated directly to Management Representative/CEO immediately. Work tasks involving the identified extreme risk must stop and implement effective control measures.
3.8 Document and Record Keeping
Objective: To define, document and communicate the documents and record keeping and procedures for all elements of The Edge Fabrication Lab WHSMS.
Scope: This covers all State Library workers who obtain, create, use, edit, review and store documents and records.
To ensure effective operation of the WHSMS, the State Library will ensure that documents and records are easily located, relevant and kept up-to-date. At The Edge Fabrication Lab, the control of document information ensures that:
- Documented information is readily available to workers and managers and that it is suitable for use; and
- Documented information is protected from loss of confidentiality about our processes, improper use or loss of document integrity.
In the control of documented information including records management, the following actions are taken to ensure documents, content and records are:
- Able to be distributed, accessed, retrieved and used in an appropriate, effective and efficient manner;
- Stored and preserved including legibility for prescribed times as per legislative or regulatory requirements;
- Version controlled and changes are documented and communicated;
- Retained and disposed of according to legislative or regulatory requirements;
- All electronic forms will be maintained and backed up as per document keeping procedure;
- All hardcopy records will be protected from damage by storage in suitable locations.
Records subjected to regulated timeframes must be kept for the required period. All other records will be kept for a period in line with the State Library record disposal schedule.
Where documented information is of external origin i.e. outside of The Edge Fabrication Lab and is necessary for the planning and operation of our processes then, the documentation will be identified. Once identified, the document will be controlled in the same manner as internally generated documented information.
Documented information retained as evidence of conformity in the form of records will be protected and stored for the length of time required by regulatory requirements. The WHS records kept by the State Library are detailed in the WHSMS Document Register.
The types of documents that can be controlled documented information include (but are not limited to):
| * HTML and Java scripted Web Pages; * WHSMS Manual; * Procedures; | * Work Instructions; * Forms; * Company templates. |
Records such as:
| * Corrective Actions; * Management Reviews; | * Visitor Complaints; * Calibration Results. |
All printed documents are considered uncontrolled.
The documents are to be approved by the Management Representative and only nominated people shall have the authority to create and modify documents. Control external documents such as law guides, standards and legislation through subscription to online databases, which maintain up-to-date versions of all materials.
Control health and safety records and worker's compensation records in accordance legislative requirements. Nominated persons shall have responsibility for holding, storing, retaining and disposition of WHS related records.
The State Library will keep records in line with specific legislative requirements for health monitoring data, injury records, risk assessments, SOP, notifiable incidents, and other specified matters. Records will be kept for the required timeframe and will be accessible for review by regulatory bodies, WHSA and HSR as appropriate.
3.9 Document and Record Keeping Procedure
The State Library has implemented a system to develop, maintain and retain WHS records that meet legislative requirements.
- Responsibilities:
At the State Library the Management Representative is responsible for ensuring that:
- There is an active Document and Record Keeping Procedure along with associated tools and resources in place and that they meet WHS and legislative requirements;
- All workers are trained and familiar with, have access to, and follow the procedure required for aspects of document and record keeping for which they are personally responsible for while working at The Edge Fabrication Lab;
- Others who are impacted by WHS at The Edge Fabrication Lab, such as additional departments are included in or consulted about document and record keeping at The Edge Fabrication Lab as required;
- Conduct review of the Document and Record Keeping Procedure as necessary.
- Informing workers and others about the requirement to appropriately record, store and manage WHSMS Manual information following the Document and Record Keeping Procedure;
- Adequately train all people in how to access, record, store and distribute WHSMS Manual information and documents in the workspace;
- Ensuring that suitable tools and resources are available to all workers to enable readily accessible and useful document and record keeping occur;
- Maintaining and managing documentation and records required by current WHS Legislation relating to WHS and worker’s compensation.
All workers are responsible for being aware of, understanding and following the Document and Record-Keeping Procedure when undertaking tasks involving workspace safety and the WHSMS Manual whilst working at the State Library.
Section 4 INCIDENT and HAZARD REPORTING
4.1 Incident Reporting
Objective: To identify and record all WHS incidents and near misses, whether or not these cause injury or damage, to minimise the potential for harm and to prevent recurrence.
Scope: This applies to everyone engaged to undertake tasks at the State Library workspaces/locations including independent contractors and volunteers.
An incident can include injury, illness, fatality, near miss, dangerous occurrence or breach of the QLD WHS Act.
The State Library is committed to reducing the frequency, impact and severity of incidents in the workspace, and to comply with legislative requirements regarding the notification and management of incidents.
All workers and any other affected person/s that are involved with or impacted by an incident at a The Edge Fabrication Lab workspace will be included in consultation and communication in relation to the incident
The State Library will also notify, manage and investigate any notifiable incidents in the workspace as determined by current QLD WHS Legislation.
The State Library will ensure the provision of coordinated incident reporting by implementing documented procedures for:
| * Emergency response and harm minimisation action; * Notification to relevant authorities of severe incidents/dangerous occurrence; * Incident reporting; * Incident investigation; * Consultation with related people (confidential where applicable); * Identification of causes; * Corrective and preventative actions; * Review of effectiveness of corrective/preventative actions; * Regular review of all incidents to identify any trends; * Report and action identified trends; * Meet legislative requirements for record keeping. |
4.2 Incident Reporting Procedure
- Responsibilities:
The State Library is responsible for ensuring that:
- There is an active procedure in place for the immediate response to and management of incidents;
- There is an Incident Reporting Procedure in place for the notification and management of incidents;
- All workers are trained and familiar with the Incident Reporting Procedure and have easy access to the report forms and procedure;
- State authority is notified immediately after becoming aware that a notifiable incident has occurred;
- So far as is reasonably practicable, that the workspace where any notifiable incident has happened is not disturbed until an inspector arrives at the workspace or any earlier time that an inspector directs;
- Conduct a review of the Incident Reporting procedure as required.
The Lead - Facilities operations is responsible for:
- Maintaining and reviewing the Incident Reporting Procedure as required;
- Train all workers in the Incident reporting procedure Assisting managers, supervisors and workers to follow the procedure when needed;
- Informing and consulting with the Work, Health and Safety Advisors (WHSA) and WHS Committee regarding incidents, in particular, notifiable incidents;
- Notification of notifiable incidents to the relevant regulator, within the prescribed timeframes;
- Ensure, so far as is reasonably practicable, that the workspace where the incident occurred is not disturbed until an inspector arrives at the workspace or any earlier time that an inspector directs;
- Maintaining records required by legislation relating to incidents.
Supervisors are responsible for:
- Informing workers and others (when applicable) about the requirement to report incidents promptly;
- Ensuring that the Incident Report Forms are readily accessible for workers;
- Complying with the Incident Reporting Procedure for incidents reported to them.
All workers are responsible for the initial reporting of incidents.
Procedure:
- Follow the State Library Emergency Response Procedure (see SLQ Emergency Response Plan) to care for workers, clear the incident area of people and secure to prevent further incident;
- Report all incidents as soon as possible to their immediate supervisor;
- When a reportable incident has occurred, Persons Responsible determines whether to preserve the workspace for investigation by the relevant regulator;
- Person involved in the incident completes an Incident Report Form;
- If the person involved in the incident is not able to complete the form, their immediate supervisor will compete it, in consultation with the involved person;
- Persons Responsible reports the incident to Management Representative, WHSA.
- Persons Responsible reports all notifiable incidents to the relevant authority, within the timeframe required by legislation;
- Persons Responsible keeps records of incidents and injuries by statutory requirements;
- Follow the incident investigation procedure, if as required.
4.3 Reporting
Objective: To provide direction for nominated persons to provide feedback via reports submitted to senior management on selected WHSMS elements.
Scope: This applies to all workers at The Edge Fabrication Lab, irrespective of their employment arrangements.
The State Library is committed to the provision of a functional and practical WHSMS and as such, understands the value maintaining feedback. The Edge Fabrication Lab will ensure effective reporting will take place via relevant individuals, including WHSA, HSR, affected workers, other duty holders/contractors to manage hazards and risks.
A proactive, planned and systematic approach to WHS reporting will help respond to change and improve health, safety and welfare outcomes. Reporting will be an on-going process conducted in line with the requirements of WHSMS and relevant legislation.
Reporting Procedure
Utilising consultative arrangements in place, and particular forms and tools, the Management Representative will report on all identified WHS issues, hazards, risks and legislated reportable incidents.
| Legislative | Non-legislative |
|---|---|
| * Injury reporting * Notifiable incidents * Worker’s compensation and return to work * Health monitoring and health surveillance * Reviews of risk controls * Consultative arrangements * Hazard Identification * Risk assessments * Other legislated matters as relevant (such as plant registration etc.) | * WHSMS performance * Results of audits * SLQ Incident reports and investigation * Preventative actions * Corrective actions |
Section 5 EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT
5.1 Emergency Management
Objective: To define the methods for managing the preparedness and response procedures for potential accidents and emergency situations that may lead to significant WHS impacts.
Scope: The Emergency Management applies to all people on The Edge Fabrication Lab workspaces. Encompass those on adjoining work workspaces, or private residences in The Edge Fabrication Lab emergency procedures and emergency responses (including evacuations) during significant or critical emergency situations or events.
The State Library will provide and maintain a safe environment for all people at the workspace and commits to preparing for potential WHS incidents and emergency situations which may arise. The procedures for preventing and mitigating emergency situations may include:
- Fires, explosions;
- Chemical spillage or leakage;
- Toxic emissions;
- Incidents as a result of equipment failure or human error;
- Medical Emergencies;
- Environmental incidents;
- Other relevant matters based on the nature of the work, hazards, size and location and number and composition of people at the workspace.
- Responsibilities:
The Management Representative is responsible for:
- Communication of policy and procedures around emergency response planning;
- Identifying who should participate in the initial risk assessment; and
- Provide guidance when necessary.
Work, Health and Safety Advisor:
- The WHSA will review the suitability and effectiveness of the emergency procedures after each accident or emergency situation.
Emergency Services Team is responsible for:
- The execution of the appropriate emergency procedures as advised;
- Ensuring the appropriate resources for the emergency response implementation are available;
- Attending emergency response as required;
- Ensuring communication of any changes is made known to Workers and any effected parties; and
- Participation in post emergency incident review processes.
Workers responsible for:
- Keeping informed and be familiar with the emergency response procedures;
- Attending any required training in relation to emergency response procedures; and
- Following the emergency procedures in case of an incident.
The Management Representative will ensure the health and safety of people by including the following:
| * Written instructions to contact emergency service organisations at the earliest opportunity; * Evacuation procedures and assembly points, firefighting and emergency equipment, marked at the workspace plan; * Building evacuation plans are displayed and not obstructed; * Emergency exits well-lit and clear of obstructions; * Fire protection equipment that is accessible and in working order; * Chemical spill containment equipment and clean up materials as appropriate; * SDS for all chemicals plus the chemical register available and current; * Trained first aid personnel and first aid equipment; * Roles and responsibilities designated and known, such as Area Wardens * Specialised training; * Specific procedures for mobility impaired persons; * Contact details for emergency services; * Consultation and co-operation with departments as applicable. |
5.2 First Aid
Objective: To minimise the adverse effects of an incident/injury by providing first aid resources and trained First Aid Officers (FAO).
Scope: This applies to all appointed FAO and any other relevant individuals at the workspace during work activities.
First aid is the provision of initial care for an illness or injury and consists of a series of simple and in some cases, potentially life-saving techniques with minimal equipment.
The Edge Fabrication Lab will use the guidelines as per relevant Code of Practice for First Aid to ensure the provision of a prompt, coordinated first aid response in these ways:
- Meet legislative requirements;
- Identify and assess the potential for an injury/incident occurring by:
- Observing tasks/work performed/work environment;
- Consulting with workers/HSR/Officers;
- Reviewing near misses and past incident reports;
- Reviewing SDS for hazardous chemicals;
- Determine suitable resources based on the nature of the work, hazards, size, location and number and composition of people at the workspace;
- Specify minimum requirements based on risk. E.g.:
- Type, contents and number of kits;
- Number and location of FAO (including remote locations);
- Appointing, training and replacing FAO as required. Provide FAO training by registered providers.
- [REF] First Aid Code of Practice 2014
5.3 First Aid Procedure
- All workers are informed and aware of the location of First Aid Kits;
- All workers are told and know the place and contact details for FAO;
- Regular audits of contents of First Aid Kit (including mobile kits) and contact details;
- The documentation of all treatment, injuries and illness;
- FAO:
- Receive adequate first aid and resuscitation training from a registered training organisation;
- Can perform first aid duties;
- Are willing to provide first aid treatment as required.
All workers will be provided access to first aid equipment and trained first aid personnel. An appropriate number of first aid personnel will be available at all times with consideration of:
- Number, location and content of equipment;
- First aid procedures;
- A number of required trained staff (including access for sub-contractors as needed). As per relevant Code of Practice for first aid equipment facilities and training for recommended number and placement of FAO;
- Signage (Design and use of first aid signs will be as per the relevant Australian Standard);
- No first aider will attempt first aid beyond their training or experience.
Location of first aid facilities and equipment detailed are on the applicable workspace evacuation plans.
Section 6 HAZARDOUS WORK
6.1 Electrical Safety
Objective: To reduce the risk of electrocution, electric shock or fires associated with the use of the electrical plant, equipment, appliances fixtures or fittings.
Scope: This applies to the risk from electric shock or electrocution to all workers, contractors, volunteers, members and visitors to The Edge Fabrication Lab workspace.
Electric shock can be received by either direct or indirect contact with an energised item, tracking through or across a medium (such as water), or by arching. Electrical burning and arching from equipment can also release toxic gases and air contaminants. Injuries from electricity can include muscular contraction (leading to falls if working at height, incidents if operating plant etc.), burns, cellular damage and death.
State Library is committed to protect workers and others from the risk of injury from the use of electricity, and from working in the vicinity of electricity. The Edge Fabrication Lab will put in place mechanisms to identify electrical hazards and risks arising from:
| * Maintenance and testing of electrical installations or equipment; * Changes or modifications to electrical installations or equipment; * The user of electrical equipment and the training and competency levels of users; * The age and condition of electrical installations or equipment; * Overhead and underground electrical services; * Electromagnetic fields; * Static electricity. |
All work on or near live or energised electrical installations and equipment requires a documented hazard identification and risk assessment.
Only licensed electricians may work on energised electrical equipment and only under strictly enforced SWMS and utilising suitable PPE and equipment.
6.2 Electrical Safety Procedure
- Responsibilities:
At the State Library the Management Representative is responsible for:
- Ensuring that any work involving the risk of electric shock or electrocution is identified and risk assessments completed and implemented as required and in compliance with the WHS/Electrical Legislation;
- Minimising the risk of electric shock or electrocution by ensuring that appropriate procedures and supporting mechanisms/systems are in place in respect of electrical hazards and risks at work;
- Ensuring that an appropriate emergency response and procedure are in place for incidents involving electricity;
- Consulting with workers and other relevant persons in regard to electrical hazards, risks and control measures;
- Ensuring that all workers are trained, competent and fully supervised at all times when there is a risk of electric shock or electrocution while working or at the workspace;
- Monitor and review electrical safety policies, procedures and emergency response as required.
The Management Representative is responsible to ensure:
- All electrically powered plant, equipment, appliances and tools that are purchased and brought onto the workspace are checked for electrical compliance and tested and tagged as per the Queensland Electrical Safety Act 2002. [REF] https://www.legislation.qld.gov.au/view/html/inforce/current/act-2002-042
- Residual Current Devices (RCD) are installed where required and portable RCD are used as and regularly tested;
- Registered, competent individuals are used to conduct electrical installation, commissioning, maintenance and repair tasks at the workspaces;
- All workers are adequately trained to visually check electrical installations, plant, equipment, appliances and tools prior to use;
- There is an effective Lock Out and Tag Out (LOTO) system in place to remove faulty or damaged electrical equipment from use, and all workers are aware of the LOTO system;
- Adequate records are kept in regard to electrical hazards, risks and all electrical items at the workspace;
- Regular monitoring and review of electrical safety procedures is completed;
- Any incidents involving electricity will be notified to the state regulator as required by the WHS Legislation.
Workers are responsible to:
- Visually check all electrical plant and equipment, including portable equipment and tools, prior to use;
- Use the correct plant, equipment, appliance or tool for the task;
- Never misuse electrical plant, equipment, appliance or tools;
- Follow SOP, risk assessments and LOTO procedures;
- Report any new electrical hazards at the workspace (isolate power source immediately if possible, to do so safely);
- Maintain records as required;
- Comply with reasonable directions given to them in respect of electrical safety.
The Management Representative will ensure electrical hazards are identified and any work conducted on, or near electrical installations will be subject to a detailed risk assessment.
Where the State Library has management control, all electrical installations at the workspace (including switchboards and temporary electrical installations) will be installed by licensed electricians.
The Edge Fabrication Lab will ensure compliance with electrical safety. An Electrical Equipment Register will be maintained in line with agreed audit timeframes.
- Any incidents involving electric shock will be notified to the State Regulator as required by the current Regulations;
- Visually check all electrical plant and equipment, including portable equipment and tools, before use;
- Report any new electrical hazards at the workspace (isolate power source immediately if possible to do so safely);
- Registered, electricians are used to conduct electrical installation, commissioning, maintenance and repair tasks at the workspaces;
- Comply with reasonable directions given to them in respect of electrical safety;
- RCD are installed where required, and portable RCD are used and regularly tested.
De-Energised Electrical Work:
- Electrical work is not to be carried out on electrical equipment while the equipment is energised, subject to the prescribed exceptions as listed in the relevant State Legislation;
- Before any electrical work is carried out on electrical equipment, the equipment must be de-energised and verified by a competent person that it is safe to work on;
- The worker carrying out the testing must understand the testing procedures and be competent in the
- use of the testing method. Panel voltmeters should not be the only method of testing to be used to determine whether an electrical part is de-energised. Additionally, each high-voltage exposed part of the equipment must be earthed after being de-energised;
- Anyone carrying out electrical work must ensure that electrical equipment that has been de-energised to allow for electrical work to be carried out cannot be inadvertently energised;
- Refer to Lock Out/Tag-Out section for support information;
- Where safe work procedures have been developed for electrical work or energised electrical work, that work must be carried out following the safe work procedure.
Electrical Equipment
All electrical equipment must be visually inspected before use and tested/tagged as per legislative requirements.
Electrical Inspections
Regular inspections will be undertaken by the management Representative (or delegate) at regular intervals to ensure all electrical leads and equipment are within test date, supplied with a compliant tag, in good condition and used/handled safely.
The scope of the inspections will include verification that electrical leads and extension leads are not placed in areas that may pose tripping hazards, on or near water or chemicals (or other deteriorating agents), not exposed to mechanical damage (from power tools) and suitable lead-stands are provided to keep leads off the ground.
6.3 Falls Prevention
Objective: To prevent falls and falling objects by implementing a risk management approach.
Scope: This applies to all workers, including contractors, volunteers and visitors of The Edge Fabrication Lab exposed to the risk from falls and falling objects, including falls from height, falls from one level to another, falls into openings, and falls on the same level (including slips and trips).
The State Library is committed to preventing injuries caused by falls and falling objects, including falls from unprotected edges and any situation where a fall may occur. This will occur through the identification of tasks and situations where a risk of fall or falling objects hazard is present and the implementation of suitable risk controls.
This includes situations when a worker or other people are:
- In or on plant, equipment or a structure that is at an elevated level;
- In or on plant that is being used to gain access to an elevated level;
- In the vicinity of an opening through which people or objects could fall;
- In the region of an edge over which people or objects could fall;
- On or in the vicinity of a surface through which people or objects could fall;
- On or near a slippery, sloping or unstable surface on which people or objects could fall.
The State Library will endeavour to eliminate or reduce the number and severity of injuries caused by falls by implementing procedures to identify and manage falls hazards and the associated risks arising from those hazards.
In consultation with relevant persons, the Management Representative will identify all tasks that have a potential for falls and falling objects.
6.4 Falls Prevention Procedure
- Responsibilities:
The Management Representative is responsible to:
- Ensure that appropriate procedures and supporting mechanisms/systems are followed in respect of falls at work;
- Assist with the identification and control of slip, trip and fall hazards such as slippery surfaces, uneven surfaces, trip hazards, unstable surfaces in work areas;
- Ensure that workers are adequately supervised at all times when working at height;
- Consult with workers and other relevant persons regarding falls hazards, risks and control measures;
- Monitor and review fall prevention policies, procedures and emergency response as required.
Workers are responsible to:
- Cooperate with reasonable directions when working in situations where there is a risk of a fall;
- Notify their manager/supervisor immediately if a new fall hazard is identified, making the area safe using a temporary control before leaving the fall hazard unattended. Use a standby person if it is not possible to make the area safe while the manager is notified and corrective action can be taken to ensure people are not placed at risk;
- Assist with the identification and control of slip, trip and fall hazards such as slippery surfaces, uneven surfaces, trip hazards, unstable surfaces in work areas;
- Use appropriate fall prevention devices, work positioning systems, fall arrest systems and PPE at all times when it is required as per the relevant workspace procedures;
- Hazard Identification:
An inspection of the intended workspace by workers will be conducted to identify fall risks (including elevated falls, falls into void/pits, falls on the same level and falling objects).
These tasks will be recorded on the Risk Register, including details of the falls hazards, the level of assessed risk and recommended control measures. The Risk Register will be regularly reviewed and updated as required.
- Risk assessment and Control:
All workers will eliminate risks wherever possible. Where risk cannot be eliminated, it will be reduced as far as reasonably practicable.
Controls will be implemented with the following priority:
(Elimination) Where possible eliminate the risk of falls by avoiding the need to work at height or adjacent to an unprotected edge
(Substitution) If elimination is not practicable, substitute a work method or process for one that is less hazardous e.g. work platform to work on machinery rather than climbing.
(Isolation/Engineering) If substitution is not practicable, isolate the person from a fall hazard by providing a passive fall restraint system e.g. safety barriers.
If higher levels controls are not practicable then, provide a work positioning system e.g. industrial rope access or a travel restraint. Note: If using travel restraint or fall arrestors ensure harness and clips are compatible; anchor points have been assessed by qualified individuals.
If a fall arrest system is utilised, emergency and rescue procedures must be developed for the system.
(Administrative) If isolation and engineering controls are not practicable, administrative controls e.g. may be used:
| * Safe work method statement * Barrier tape | * Warning signage |
(PPE) e.g. safety harness with lifelines, non-slip shoes
Note 1: More than one of these measures to reduce a risk can be used. E.g., engineering controls like edge protection can be implemented with administrative controls like training and this Safe Work Method Statement (SWMS), while wearing PPE (non-slip shoes).
Risk controls will be maintained to ensure they are suitable for the task, installed/used correctly and they remain effective for the duration of the task.
Working adjacent to unprotected edges
All workers will manage the risks associated with falls when working adjacent to unprotected edges.
When working adjacent to unprotected edges at a minimum the following will apply (additional controls may be put in place as a result of a risk assessment):
- Install warning signage and ensure administrative procedures are in place and understood by all workers;
- Inform all workers and visitors of hazardous area;
- Control access to the area at all times;
- Maintain safe distance from edge;
- Keep trip hazards away from edges;
- Wear appropriate non-slip covered footwear;
- Be aware of ground conditions e.g. slippery, oily, or uneven surfaces;
- Never walk backwards when working adjacent to unprotected edges;
- Do not rush, run or play around;
- Use deliberate motion when working;
- Keep work area clear of trip hazards;
- Keep floor clean and clean up spills immediately;
- Never lunge for dropped objects (maintain balance at all times).
6.5 Hazardous Manual Tasks
Objective: To eliminate or reduce the number and severity of injuries caused by hazardous manual tasks.
Scope: This applies to all workers, contractors and volunteers at The Edge Fabrication Lab exposed to the risk from hazardous manual handling tasks.
Some hazardous manual handling tasks can lead to Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSD) or other injuries for workers, such as sprains and strains, back, joint or bone injuries, nerve injuries or compression, muscular and vascular disorders, hernias or chronic pain. MSD can occur suddenly or over an extended period.
The State Library is committed to preventing injuries caused by manual tasks through the identification of hazardous manual tasks and implementation of suitable risk controls.
Some manual handling tasks can be considered hazardous, such as tasks involving any of the following characteristics:
- Repetitive or sustained application of force, awkward positions or movement;
- Use of high force;
- Exposure to continued vibration;
- The handling of unstable or unbalanced loads or loads which are difficult to grasp or hold.
The State Library has implemented strategies to minimise the risk of worker injury from hazardous manual tasks including:
- Identifying manual tasks that are hazardous;
- Eliminating hazardous manual tasks at the workspace whenever possible to do so;
- Assessing the risks of MSD and other injuries associated with hazardous manual tasks;
- Implementing suitable risk control measures to lower the potential for worker injuries in respect of manual handling tasks;
- Monitoring and reviewing risk control measures when appropriate;
- Providing training and resources to increase worker knowledge about manual handling;
- Developing and implementing work procedures designed to lower risk from hazardous manual handling tasks;
- Providing manual handling equipment appropriate for performing the job tasks;
- Consult with workers concerning hazardous manual handling issues.
6.6 Hazardous Manual Tasks Procedure
- Responsibilities:
The Edge Fabrication Lab Management Representative is responsible for ensuring:
- The identification and assessing of any task requiring manual handling;
- Risk assessments are carried out for all hazardous manual handling tasks;
- Safe work procedures are in place to eliminate or reduce and control the risk of injury to workers due to manual handling;
- Provision of adequate and appropriate training to workers in respect of manual handling;
- Hazardous manual handling tasks and related procedures are monitored and reviewed as required.
Workers are responsible to:
- Assist and cooperate with the identification of hazardous manual handling tasks in the workspace;
- Attend manual handling training when required;
- Use correct manual handling procedures when needed and follow safe working procedures.
Hazardous manual handling tasks will be identified by:
- Discomfort surveys;
- Observing tasks;
- Breaking tasks down where required;
- Hazard reports;
- Seeking worker input;
- Consulting with an ergonomic assessor or others with specialised knowledge and skills if needed.
- Risk Assessment:
If a risk assessment is undertaken, it will be documented and take the following risk factors into account:
- Duration and frequency;
- Forces exerted;
- Sources of risk (such as layout of workspace, loads, tools, systems of work, environment).
Controls will be implemented using a hierarchy of controls. E.g.:
- Eliminate task;
- Substitute for less hazardous options;
- Isolate people from risk;
- Use engineering controls;
- Develop procedures and administrative controls;
- Provide Information, training and instruction.
Risk controls will be reviewed whenever:
- Control is no longer effective;
- Any change is likely to introduce new or different hazards that current controls will not adequately address;
- Identification of a further hazard or risk;
- Results of consultation indicate a review is needed.
6.7 Hearing Protection and Audiometric Testing
Objective: To comply with relevant current WHS Legislation in respect to hearing protection and audiometric testing.
Scope: This covers all people engaged at The Edge Fabrication Lab workspaces/locations exposed to the risk of hearing loss due to noise levels above the exposure levels
The State Library acknowledges that it has specific obligations under current Legislation to manage the risks of hearing loss associated with exposure to noise at the workspace. As such, systems will be put in place to:
- Ensure worker exposure to noise does not exceed the Noise Exposure Standard; [REF] Managing noise and preventing hearing loss in the workplace Code of Practice 2018
- Provide audiometric testing to a worker who is frequently required to use personal hearing protectors to protect the worker from hearing loss associated with noise that exceeds the exposure standard.
The following tasks will form the framework to identify and mitigate risks in respect of noise and hearing loss:
- Identify situations where a workers' exposure exceeds the Noise Exposure Standard;
- Assessment of the extent of the risk associated with the work in respect of hearing loss;
- Establishment of noise monitoring and assessment systems and interpretation of noise monitoring results;
- Establishment of control measures using the hierarchy of controls;
- Regular consultation with workers exposed to noise at the workspace;
- Documented policies to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of the risk control measures.
Noise assessments and audiometric testing will be done by a suitably qualified person and will be carried out following the legislative requirements and the procedures outlined in the relevant Australian Standard. The personal information of individual workers, including medical reports and audiometric testing results, will remain confidential at all times between the senior manager and the worker. Workers will be supplied the results of audiometric testing accompanied by a written explanation of the meaning and implications.
6.8 Hearing Protection
If using hearing protection, supervisors will ensure:
- Everyone wears hearing protection throughout exposure to noise;
- It is suitable for the type of working environment and the work tasks;
- It is comfortable and correctly fitting for the worker;
- It is regularly inspected and maintained to ensure it remains in good, clean condition;
- Only wear disposable ear-plugs once;
- Use signs indicating “Hearing PPE must be worn” areas.
Workers are responsible to:
- Cooperate with reasonable directions in respect of noise and hearing loss prevention;
- Wear appropriate hearing protection as per the relevant workspace procedures;
- Be familiar with, understand and follow this procedure.
6.9 Safe Operating Procedures (SOP)
Objective: To outline a process to assist with the development of workspace-specific Safe Operating Procedures (SOP) for tasks and processes that have the potential to cause harm to people, equipment or the environment.
The State Library is committed to the use of SOP when their use is indicated as a result of a risk assessment. Where the requirement for a SOP is identified, a SOP will be developed and maintained by those undertaking the activity (developed in consultation with manufacturers or users).
SOP will be used as the format to write safety instructions for hazardous tasks. SOP will be site/task specific and detail all steps involved in the task.
A SOP for The Edge Fabrication Lab will be used to
- Outline a safe method of work for a specific activity;
- Provide an instructional document that must read and understand before commencing the activity;
- Assist in meeting legal requirements;
- Provide evidence in auditing and inspection;
- Satisfy contractual requirements.
6.10 Safe Operating Procedures (SOP) Procedure
- Responsibilities:
The Edge Fabrication Lab takes responsibility for ensuring that all users are aware of, trained in, and understand the contents of the SOP.
Management Representative - arrangements will be put in place to follow SOP. These include:
- All hazardous equipment and tasks has an SOP;
- All users are aware of, trained in, and understand the contents of SOP;
- Make sure adequate resources are available;
- Make all SOP available;
- Adequate supervision;
- Consultation, information and training;
- Users competency assessments;
- Periodic reviews of the SOP are carried out and updated where necessary.
Users are responsible for complying with all rules and regulations concerning safe work practices and all requirements stated on the SOP.
- Procedure:
SOPs will be developed in consultation with all relevant persons and risk assessment/controls will be developed following the risk management protocols outlined in this manual. Everyone involved in the task will be trained in the content of the SOP and all risk controls detailed therein.
Should the task/activity be new or involve use of new plant/equipment external expertise may be required to complete the SOP and this should be sought where applicable. Elected HSR will be consulted where applicable.
SOP will be written in a concise, logical, step-by-step, easy-to-read format with sufficient detail to ensure that someone with limited experience can successfully carry out the procedure in a safe manner with limited supervision or unsupervised. The SOP may reference other material such as operating manuals or another SOP.
For each step in the work task, list the most appropriate risk control measure that will eliminate or minimise the risk to the workers completing the work task.
The SOP should be written by a member of staff who has good knowledge of the task and has performed the particular task. Consultation with others involved in the task is recommended.
The SOP should include:
- The name and purpose of the task/process;
- Definition of any acronyms or specialised terms;
- Potential hazards and associated risks of the task/process;
- Clear and simple instructions for undertaking the task/process in a safe manner;
- Any PPE required to be worn while undertaking the task;
- Emergency procedures and shutdown.
All SOP will be reviewed on a regular basis and if necessary, revised:
- If the results of consultation indicate that a review is necessary, or if a health and safety representative request a review;
- After an incident or near-miss (control measure was not effective in controlling the risk);
- If the task/activity changes;
- When a new hazard or risk is identified;
- Where the equipment or plant used in the SOP changes;
- If there is a change to legislation, standards or codes of practice.
A SOP Register will be used to track the number and type of SOP and review timeframes.
Section 7.1 PLANT, EQUIPMENT and STRUCTURES
7.1 Facilities Management
Purpose: To identify and reduce risks by providing and maintaining a safe environment with adequate facilities and, to provide adequate resourcing to maintain these facilities.
The State Library understands that workers and members of the public are more at risk of being involved with or causing an accident if the facilities are not suited to the work environment. The organisation is committed therefore to providing and maintaining a physical work environment that is without risks to health and safety. [REF] Managing the work environment and facilities Code of Practice 2011
The State Library will:
- Ensure the health and safety of workers and visitors to the workspace with regard to facilities management;
- Engage with workers on facilities requirements;
- Identify and assess hazards arising from facilities management;
- Eliminate or control facilities related risks; and
- Provide information and instruction on managing facilities.
- Responsibilities:
The Edge Fabrication Lab Management Representative is responsible for:
- Providing adequate facilities for the workspace;
- Ensuring the health and safety of workers and visitors to the workspace with regard to facilities management;
- Engaging with workers on facility requirements;
- Identifying and assessing hazards arising from facilities management;
- Eliminating or controlling facility related risks; and
- Providing information and instruction on managing facilities.
Workers, and others, are responsible for:
- Engaging with relevant managers and supervisors in relation to developing facilities requirements;
- Cooperating with The Edge Fabrication Lab policies and other relevant WHS systems;
- Engaging with relevant managers and supervisors in relation to facilities management;
- Reporting any hazards and risks relating to the use of facilities;
- Ensuring that their behaviour does not damage workspace facilities or prevent their use by others.
7.2 Facilities Management Procedure
To eliminate, reduce or manage the risk associated with facilities management the Management Representative will consult with workers on facility requirements and Identify and assess hazards arising from these facilities to ensure:
- The layout of the workspace allows people to enter and exit the workspace and to move within it safely;
- Floors and other surfaces are maintained to allow work to be carried out safely;
- That work areas have sufficient space for work to be carried out in a safe manner;
- There is suitable and sufficient lighting to enable users to carry out work safely;
- There is suitable and sufficient ventilation to enable users to carry out their work safely; and
- There are sufficient facilities for drinking and wash water, toilets and rest areas.
In participation with users the management Representative will ensure that these facilities are sufficient in number and are maintained to be clean, safe and in good working order with consideration of:
- The type of the work being carried out at the workspace;
- The nature of hazards and risks at the workspace;
- The size, location and number of people at the workspace (with consideration of gender and/or physical disabilities).
If the nature of the work is such that the following applies, The Edge Fabrication Lab will also ensure there are suitable facilities for:
- Washing the body;
- A place to change clothes that become contaminated or wet;
- Keeping clothes that will not be used at work clean and dry;
- An opportunity for rest when work involves continuous working on the feet; and
- Control of airborne contaminants as closely as possible to their source by being treated or carried off.
7.3 Plant and Equipment
Objective: To minimise risks associated with plant, whether owned, leased or hired, are eliminated or reduced as far as practicable, and injuries to workers including contractors, volunteers and visitors.
Scope: This procedure applies to all workers who, in the course of their duties, acquire (purchase/hire/lease/loan/donate), install, use, operate, store, maintain or dispose of plant and equipment on behalf of, or while working for the State Library at The Edge Fabrication Lab.
The Edge Fabrication Lab recognises its responsibility to provide and maintain a safe workspace, including the identification of hazards and control of risks associated with the plant.
The Edge Fabrication Lab will endeavour to prevent injury and eliminate hazards associated with the plant by ensuring:
- No plant is brought onto workspace and commissioned unless there are health and safety risk controls;
- Suitably qualified persons install and commission plant, and monitor risks during these activities;
- Plant is used only for its designed purpose unless an assessment has been carried out by a suitably qualified person for any other proposed use;
- Plant complies with legislative requirements for guarding, operator controls, cleaning, maintenance and testing as required; [REF] Managing the Risks of Plant in the workplace Code of Practice 2013
- A documented system is developed and implemented to identify hazards, conduct risk assessments where needed, and select suitable controls for installation, commission, use, cleaning/maintenance and decommissioning/dismantling. Select risk controls following a hierarchy of control:
| * Elimination; * Substitution; * Engineering controls; | * Isolation; * Administrative controls; * Safe work procedures; |
- Provide adequate training, information, instruction and supervision as required.
- Risk controls will be reviewed when:
- Control is no longer effective;
- Before any change likely to introduce new or different hazards that current controls will not adequately address;
- Further hazards and risks have been identified;
- Results of consultation indicate a review is needed;
- Where requested by workers or HSR;
- As per manufacturer’s instructions.
7.5 Plant and Equipment Procedure
This procedure addresses the management of safety issues involved with the operation, inspection, maintenance, checking, repair, servicing, testing and monitoring of plant and equipment.
- Responsibilities:
The Management Representative is responsible for ensuring there is a safe system in place for all aspects of the management of plant and equipment, which meets both the purpose of this procedure and the requirements of current WHS Legislation.
Workers who are required to use, operate and/or maintain plant and equipment must ensure they follow the SOP steps listed. Workers will be provided with information and training to enable them to comply with the procedure.
- Procedure:
- Acquisition:
- Follow the State Library Purchasing Procedure for the purchase of all plant and equipment;
- Licensing and Certification:
- Determine the Certification requirements of plant and equipment, and licensing requirements for operators, as required by the relevant Authorities (must be done prior first use at The Edge Fabrication Lab);
- Worker Training and Qualification – Plant is requiring Certification:
- Workers who will be responsible for the management, operation, use, maintenance and disposal of plant and equipment that involves Certification hold current operator's licenses and are trained and competent as required by the relevant Authorities;
- Worker Training – Equipment not requiring Certification/Licencing:
- Workers must be trained to safely operate the equipment by a person who is suitably competent/experienced in its operation;
- If an experienced person is not available, the worker’s manager must ensure the manufacturer’s operating instructions are available, read and understood by the worker before operation commences;
- A Safe Operating Procedure shall be explained and demonstrated during training, including any risk assessment for the equipment;
- The workers must be able to demonstrate the safe operation of the equipment under supervision before being allowed to operate the equipment unsupervised;
- Maintenance and Pre-start checks:
- Before any plant or equipment is cleaned, serviced, repaired or modified appropriate control measures, including engineering controls where applicable, must be implemented to prevent accidental or deliberate operation. E.g., isolation from electricity, removal of keys, lock out and tag etc. Pre-operational checks must be conducted on all plant before use. These may be daily, weekly, monthly, six monthly and annual checks as recommended by the manufacturer;
- All plant and equipment will be stored, cleaned, serviced, repaired and maintained as per the manufacturer’s recommendations;
- Return of plant or equipment to service:
- Make a record of any inspection, maintenance, repair or alteration to plant on the Plant and Equipment Register/Maintenance Log;
- A qualified person is to verify and approve that the plant or equipment is safe for use, before it being used again after having been taken out of service;
- If plant or equipment has been locked out or tagged, the qualified person will re-commission the plant or equipment and advise workers that it is back in service and is safe to use;
- Testing and Tagging:
- Plant will be inspected/checked by an Authorised Person and will have inspection tags/labels placed on them as required;
- Equipment will undergo regular checks to ensure it is fully functional and safe to use;
- Plant or equipment that fails to test, or is found to be unsafe, damaged, will be removed from service and will be locked out/tagged as appropriate;
- Keep records of all testing and tagging of plant and equipment;
- Operation:
- All plant and equipment must be used or operated as per the manufacturer’s recommendations;
- Workers will follow the guidance provided in any Safe Work Procedures (SOP), Risk Assessments (RA) and as outlined by on-the-job training and supervision as required;
- Under no circumstances is faulty or damaged plant or equipment to be used;
- Disposal:
- Before disposal, plant and equipment may need to be rendered inoperable, or de-commissioned to leave it safe for disposal. De-commissioning as required;
- Dispose of plant and equipment in an environmentally suitable manner and per Local Authority requirement.
7.5 Plant Lock Out/Tag Out (LOTO)
Objective To avoid hazards related to accidental start-up, movement of a machine part or the uncontrolled release of energy.
Scope: This procedure applies to all workers who, in the course of their duties, may be required to perform a LOTO procedure.
The State Library recognises its responsibility to provide and maintain a safe workspace, including the control of risks associated with accidental start-up, movement of a machine part or the uncontrolled release of an energy system.
The State Library will endeavour to prevent injury and eliminate hazards associated with a LOTO process by ensuring:
- A LOTO procedure is in place;
- LOTO equipment is available for use (e.g. safety tags, locks etc.);
- Adequate training, information, instruction and supervision of LOTO procedures is provided;
- All workers undertaking a LOTO procedure are licensed where required (e.g. electrical);
- Safe work procedures e.g. SOPs for items of plant and equipment that need LOTO operations are developed and put in place.
Definitions:
Lockout - A device is placed on, around, or through an energy-isolating mechanism to lock it in a safe position.
Tag out - The process by placing an energy-isolating device for an item of plant/equipment in the off position, and a written warning tag is attached. A 'tag out' should be used only when the energy-isolating device is not capable of being locked out, e.g. A small item or power tool.
Lockout-Tag out (LOTO) - A device is placed on, around, or through an energy-isolating mechanism to lock it in a safe position and attach a written warning tag. Locks and Tags must be substantial enough to prevent casual or accidental removal. Locks and tags must also identify the worker applying and using the device.
| Cause | E.g. | Cause | E.g. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fluid | Water, steam, hydraulic fluid | Mechanical | Gears linkages, rings, flywheels |
| Gas | Pressurised gases, vacuum | Chemical | Volatile chemicals, radiation |
| Pneumatic pressure | Compressed air | Electrical | Mains, generator |
7.6 Plant Lock Out/Tag Out (LOTO) Procedure
- Responsibilities
The Edge Fabrication Lab Management Representative is responsible for ensuring that:
- A safe system in place for management of LOTO procedures;
- Standard Operating Procedures for shutdown-isolation-working under power LOTO for unit specific plant or equipment instructions. (Document instructions for the LOTO of plant/equipment by engaging with HSR /workers who work with the relevant plant or equipment). These specific instructions must contain the following information:
- Method and order of identifying, locating, isolating, and locking out or tagging out each energy source;
- Process of verifying a zero-energy state, including testing of the energy state;
- Method and order of reconnecting each energy source to the system;
- Workers responsible for the LOTO operation hold current licenses and are fully trained and competent to undertake the task;
- Equipment not requiring licensing:
- Workers are trained to safely operate the equipment by a person who is suitably competent/experienced in its operation;
- If an experienced person is not available, the worker’s manager must ensure the manufacturer’s operating instructions are available, read and understood by the worker before operation commences;
- A Safe Work Procedure shall be explained and demonstrated during training, including any risk assessment for the equipment;
- The workers must be able to demonstrate the safe operation of the equipment under supervision before being allowed to operate the equipment for LOTO purposes unsupervised.
- A copy of the following procedure is provided to all contractors working at The Edge Fabrication Lab before they undertake work;
- The LOTO Procedure is implemented when necessary and, that all workers are familiar with the procedure, and that the process is followed;
- A Safe Work Procedure is explained and demonstrated during training, including any risk assessment for the equipment;
- The workers can demonstrate the safe operation of the equipment under supervision before being allowed to operate the equipment for LOTO purposes unsupervised.
Workers are responsible for ensuring:
- Reasonable care for their health and safety;
- Reasonable care for the health and safety of others;
- They follow the LOTO procedure at all times.
Contractors:
All contractors working at The Edge Fabrication Lab workspace must comply with this procedure (exceptions agreed only in writing). Contractors are expected to provide all locks, tags, and other devices required for LOTO associated with their contract (exceptions in writing for of LOTO items unique to The Edge Fabrication Lab). No Contractor may participate in work on plant or equipment until they have obtained and applied the required devices.
- LOTO Procedure:
- Acquire Isolation Permit to Work;
- Notify all affected workers that a lockout is required and that it will be undertaken at a particular date and time;
- Identify all energy sources and hazards by conducting a risk assessment. Review any written LOTO instructions if applicable;
- If the equipment is in operation, shut it down by following the standard procedure (e.g. stop button);
- Identify devices used to maintain the energy source (electrical, hydraulic, gas, other) and disconnect or isolated from the equipment;
- Lockout energy isolating devices with an appropriate lock and tag;
- Ensure work areas is clear before dissipating any stored energy (e.g. hydraulic systems, compressed air, steam or water pressure;
- Ensure work areas is clear before testing plant or equipment is isolated;
- Operate the start button or other operating controls (if applicable) to ensure the equipment will not operate and is in a zero-energy state;
- Return operating/start-up controls to off/neutral position after the test;
- The equipment is now locked out and tagged;
- Undertake the maintenance or servicing task.
Restoring Equipment to Service Procedure:
- Notify all affected workers that the plant/equipment will be back in service and that it will be undertaken at a particular date and time;
- Ensure work areas is clear before devices used to maintain the energy source (electrical, hydraulic, gas, other) are reconnected;
- Remove all tools and parts;
- Re-secure all guards;
- Remove all locks and tags;
- Restore energy to equipment;
- Inform Supervisor/Manager/other staff that all isolation has been removed and equipment/plant has been returned to operational status.
7.7 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Objective: To protect workers from workspace hazards by developing a system to manage the selection, use and maintenance of PPE where required.
Scope: This covers all workers required to wear PPE.
The purpose of PPE is to protect the workers of the State Library from exposure to workspace hazards. The State Library will provide workers with suitable PPE for the workspace or where required for specific tasks at no cost to the worker.
The State library will:
- Ensure PPE is suitable concerning:
- Nature of the work;
- Hazards associated with work;
- Appropriate size and fit;
- Reasonably comfortable to wear for type of task and intended duration of the job;
- Maintained, repaired and replace to ensure it remains effective in minimising risk to workers;
- Select quality PPE to meet relevant Standards; [REF] How to Manage Work Health and Safety Risks Code of Practice 2011
- Provide training, guidance, and assistance to supervisors and workers on the proper selection, use, care, and cleaning of approved PPE;
- Develop and make accessible, instructions for selection, use, maintenance, and cleaning of PPE;
- Designate areas where PPE is required and display signs;
- Periodically re-evaluate the suitability of previously selected PPE;
- Develop a system to inspect PPE to ensure it is clean, hygienic and in good working order;
- Conduct inspection and checks to make sure workers are using provided PPE;
- Review, update and conduct PPE suitability assessments whenever:
- A job changes;
- Using new equipment;
- There has been an incident;
- A supervisor, worker or Health and Safety Representative requests it;
- Or at least every year.
- Maintain records of PPE assignments and training.
PPE is not a substitute for more effective controls, only consider PPE when higher means of protection are not reasonably practicable, or in addition to higher control measures.
7.8 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Procedure
- Responsibilities:
The Edge Fabrication Lab Management Representative is responsible for ensuring that:
- Providing suitable PPE to protect workers from hazards and risks;
- Ensuring suitable mechanisms are in place for the acquisition, use, maintenance and storage of PPE.
- That all items of PPE that are acquired meet relevant Australian Standards;
- PPE to be worn for specific work tasks is identified using risk assessments, SOP, and Operational Manuals etc.;
- Workers are provided with appropriate PPE for the tasks they perform;
- Workers are trained and competent in the selection, use and maintenance of PPE;
- Workers wear and use allocated PPE at all times and correctly while working;
- Repair and replaced PPE when required;
- Locate and display signs in areas where PPE must be worn;
- Keep records in the PPE Register.
All workers at the workspace are required to:
- Wear PPE as appropriate and/or instructed;
- Not misuse or deliberately damage PPE;
- Inform management of any damage, defect or contamination of PPE that may render the PPE unusable.
- Procedure:
PPE will be issued to workers and others when:
- A hazard cannot be eliminated or reduced by controls other than the use of PPE;
- Specific protection required by Risk Assessments, Safe Work Procedures;
- It is identified or determined by relevant legislation, Code of Practice or Australian Standard.
Individuals must wear PPE:
- As and when instructed by managers/supervisors;
- Recommended by a Safety Data Sheet, Risk Assessment, SOP, or Operational Manuals etc.;
- Following induction and competency training and relevant procedures;
- Following the manufacturer's guidelines.
PPE must:
- Be appropriate for the type of work and give adequate protection from the hazard;
- Not create additional hazards or risks for the user, or for others;
- Be compatible PPE (e.g. Hardhat and ear protectors);
- Correct fit, comfortable and be easy to use;
- Not interfere with any medical conditions of the user;
- Comply with the relevant Australian Standard;
- Be kept in good condition and cleaned after each use;
- Be replaced when required.
7.9 WHS Purchasing
Objective: To give consideration when purchasing equipment, materials or chemicals, which may have an adverse impact on health and safety.
Scope: This applies to all workers who have roles and responsibilities relating to purchasing, hire, lease, or donations.
The most effective way of reducing risks to health and safety in the workspace is through elimination. The Edge Fabrication Lab is committed to eliminating hazards associated with purchased items of plant, equipment, chemical substances and other materials into the workspace by the implementation of a WHS purchasing.
Purchasing and acquisition of all items must take into account the State Library purchasing policies, legislative safety requirements and requires assessment by the appropriate manager initiating the purchase, ensuring conformance to The Edge Fabrication Lab WHSMS policies and current WHS Legislation.
The Edge Fabrication Lab will implement the following:
- Specifying WHS requirements with supplier before purchasing;
- Determining WHS risks before purchase;
- Conducting plant/equipment and chemical risk assessments as appropriate;
- Obtaining WHS information, SDS, manuals, instructions, design specifications;
- Comply with legislation, Australian Standards, environmental law;
- Consider worker capability/training/licensing requirements;
- Appropriate risk control strategies in place for use, transport, disposal and storage;
- Choosing best practice/least hazardous options;
- Review of purchased item before accepting admission into workspace;
- Adequate documentation/records will be kept.
7.10 WHS Purchasing Procedure
- Responsibilities:
The Management Representative is responsible for ensuring there is a safe system in place for the purchase, acquisition and procurement of plant, equipment, materials and chemicals for use in the fabrication lab, which meets both the purpose of this procedure and the requirements of WHS and environmental legislation.
The Manager is responsible for implementing the Purchasing Procedure and that all workers are familiar with and follow the State Library purchasing procedures.
Workers who are required to acquire equipment, materials or chemicals must ensure they follow the steps listed below and, as needed, to follow those instructions at all times. Workers must be provided with information and training to enable them to comply with this procedure.
- Procedure:
- Follow SLQ Procurement Framework
- Determine purchase need for the item and the potential supplier/s;
- Gather information about the item in respect of safety (use, storage and disposal) including potential hazards or risks;
- Obtain information from Codes of Practice, SDS, Operational Manuals, Safe Work Procedures, Australian Standards, Industry Standards, suppliers, manufacturers etc.;
- Use information to determine if there are any associated hazards or risks for the item;
- Conduct a formal risk assessment if appropriate;
- Submit all information regarding the purchase of the article, including any risk assessment to the Management Representative or WHSA;
- The Management Representative or WHSA assesses the information and determines if the acquisition will proceed or not;
- If purchase is not approved to continue – investigate an alternative item which is less hazardous, and/or seek further information as to what would be a safer acquisition of the article;
- If the purchase is proceeding - attempts to eliminate any new hazards from being introduced into the workspace should be tried before supply. Where this is not possible, risk control measures shall be determined and implemented to minimise the risk of injury or illness;
- Before the first use of the item supervise all workers, who use, store, handle the plant while being trained in its safe use, ensuring they are aware of the hazards and risks associated with it.
7.11 Environmental Sustainable Procurement
Objective: To provide the State Library with:
- An effective way of procuring goods and services utilising a sustainable manner;
- Guidance for reduction of environmental, social and ethical impacts when purchasing goods and services;
- A framework to ensure that purchasing is carried out in a fair and equitable manner;
- Ensuring value for money in the procurement of goods and services;
- Improved product and service efficiency;
- Compliance with all regulatory obligations;
- A model to encourage suppliers to adopt cleaner technologies and produce sustainable goods and services.
Scope: This applies to the purchase of all goods and services made by or for The Edge Fabrication Lab.
This outlines the commitment of the State Library to efficient, effective, economical and sustainable procedures in all procurement activities. The following principles will be observed throughout all stages of the procurement process at the State Library to ensure optimal environmental, social, and ethical outcomes aligned to The Edge Fabrication Lab policies and legislative requirements.
- Principal use of resources – Determination of how the goods or service are to be used (basis for need, efficiency, WHS impact);
- Minimum purchasing - purchasing only occurs after determining that the goods or service are necessary;
- Locality - sourcing goods or services from local suppliers to assist local investment and economic sustainability;
- Ethical sourcing - whenever possible purchasing goods that have been fairly traded;
- Design - design efficiencies, reuse/recycle potential;
- Minimum greenhouse gas emissions – operating efficiencies, “green” energy;
- Minimum toxicity - purchase of goods that are free of toxic or polluting materials and chemicals;
- Minimum habitat/fauna/flora destruction – such as “green” products, biodegradability;
- Packaging - minimum packaging is used and that packaging is reused and/or recycled;
- Minimum waste - avoid, reduce, reuse and recycle;
- Maximum water efficiency;
- Waste management – issues associated with disposal are assessed and controlled prior to purchase;
- Life Cycle Costing – assessment of the environmental, social, economic cost of a good/service during its lifetime.
- Responsibilities
The Edge Fabrication Lab Management Representative is responsible for ensuring that:
- Strategies are adopted to avoid unnecessary expenditure and consumption of goods and services
- Goods and services selected have a lower environmental, social and ethical impact compared to competing goods and services;
- All procurement practices comply with relevant legislation;
- Purchasing decisions support and are consist with the company’s core values, policies and procedures;
- Purchasing is to be undertaken on a competitive basis with all potential suppliers being treated impartially, fairly, honestly and consistently;
- Any actual or perceived conflicts of interest are to be identified, disclosed and appropriately managed;
- Accountability for all procurement decisions is taken and ethical conduct is maintained
Workers who are required to undertake procurement functions on behalf of the State Library for The Edge Fabrication Lab should familiarise themselves and maintain currency with the State Library Sustainable Procurement.
Section 8 HAZARDOUS CHEMICALS and DANGEROUS GOODS
8.1 Hazardous Chemicals and Dangerous Goods
Objective: To ensure that hazards associated with the use, handling, generating, storage and disposal of hazardous chemicals and dangerous goods are identified, assessed and controlled as far as reasonable.
Scope: This applies to all workers who have roles and responsibilities concerning hazardous chemicals and dangerous goods that are acquired, generated, used, stored and disposed of at The Edge Fabrication Lab workspaces.
The State Library is committed to providing a safe environment for workers (including contractors and volunteers), members, visitors and members of the public and the environment about hazardous chemicals and dangerous goods and to comply with the relevant legislative requirements.
The State Library will ensure a systematic approach to managing health and safety risks associated with hazardous chemicals and dangerous goods. consider the properties of the chemicals, physical reactions and health effects, nature of work and other plant or structures that may cause adverse reactions to the hazardous chemicals and dangerous goods.
The State Library will implement a system to manage all hazardous chemicals and dangerous goods to include:
- Register of hazardous chemicals and dangerous goods;
- Legislative requirements for quantities:
- Manifest;
- Placarding;
- Consultative approach to chemical risk assessments;
- Suitable storage facilities;
- Substitution with less hazardous chemicals and dangerous goods where possible;
- Access to Information:
- Correct Labelling;
- SDS (accessible and current – within 5-year issue date);
- Safe Work Instructions;
- Results of chemical risk assessments;
- Training and Supervision;
- Responsible persons;
- Health surveillance and health monitoring where required;
- Suitable PPE;
- Regular audits of system;
- Chemical emergency response and procedures.
The Edge Fabrication Lab will review risk controls if there are amendments to SDS, changes to work practices with hazardous chemicals and dangerous goods or if health monitoring results indicate exposure, atmospheric monitoring reveals concentrations have exceeded the exposure standard for the chemicals.
8.2 Hazardous Chemicals and Dangerous Goods Procedure
- Responsibilities:
- The Edge Fabrication Lab Management Representative is responsible for ensuring that there are safety systems and mechanisms in place to protect workers who may be exposed to Hazardous Chemicals or Dangerous Goods while undertaking tasks for The Edge Fabrication Lab, per the requirements of Labelling of Workplace Hazardous Chemicals Code of Practice 2011
The Management Representative is responsible:
- For implementing legislative requirements relating to hazardous chemicals and dangerous goods, and adopting appropriate support strategies, policies, procedures and tools according to the Manual, and these actions shall include the identification, assessment, elimination and control of risks arising from hazardous chemicals and dangerous goods;
- For developing procedures to control or combat an emergency situation or environmental threat involving Hazardous Chemicals or Dangerous Goods. When required seek additional advice from competent persons in the development of these emergency procedures.
In the case of an emergency involving Hazardous Chemicals or Dangerous Goods the Management Representative:
- Assists workers to assess the situation, determine and carry out the appropriate action required to ensure the immediate health and safety of all workers and visitors, including the evacuation of areas considered to be dangerous or damaged by chemicals and overseeing administration of first aid to any casualties;
- Liaises with Emergency Services personnel;
- Notify the relevant and environmental authorities as required by legislation;
- Ensures WHSA has been notified;
- Coordinates the implementation of any corrective actions necessary to prevent any repeated or similar incident;
- Monitors and re-assesses the situation and maintains incident reports and associated documentation.
Individual workers in the workspace have a responsibility to co-operate with The Edge Fabrication Lab policies and procedures concerning their tasks relating to:
- Chemical management systems and practical mechanisms;
- Chemical risk assessment processes and the development of safe work practices;
- Consultation about hazardous chemicals and dangerous goods;
- Training and Induction;
- Monitoring and health surveillance;
- Chemical emergency drills and chemical incident response procedures;
- Assistance with emergency evacuations and first aid administration if trained and competent;
- Incident notification.
- Procedure:
- The acquisition of chemicals as per the State Library Purchasing and procedure;
- All chemicals at the workspace are identified and listed on the Hazardous Chemicals/DG Register;
- Obtain a SDS for each chemical product or material and check for compliance with the relevant Code of Practice. SDS are easily accessible for workers and others as required;
- A Chemical Register is completed and maintained as current for all Dangerous Goods used;
- Chemical placards and signage is installed at the workspace, as required by the applicable legislation
- Chemical placards and signage meets Australian Standards;
- Chemical risk assessment, using Chemical Risk Assessment Form, is conducted for all chemicals (or materials) identified as being classified as a Hazardous Chemical or a Dangerous Good as per the relevant Code of Practice;
- Implement appropriate risk controls for the acquisition, use, generation, handling, storage and disposal of assessed chemicals;
- Obtaining licenses and permits required for restricted or regulated chemicals;
- Chemical storage is available at the workspace, taking into consideration such factors such as compatibility, quantities to be stored, ventilation, security etc.;
- Maintain documentation in respect of Hazardous Chemical and Dangerous Goods as required by legislation;
- Maintain incident reports, investigation reports and Workers Compensation documentation concerning matters related to hazardous chemicals and dangerous goods for a minimum period of thirty (30) years after the incident or injury date;
- Regularly monitor and review chemical management policies, procedures, mechanisms and incidents at The Edge Fabrication Lab.
8.3 Health Surveillance
Objective: To reduce the risk to workers (including contractors and volunteers) members and visitors from adverse exposure to physical hazards and hazardous chemicals, by providing a framework to conduct and monitor Health Surveillance in the workspace.
Scope: This applies to all The Edge Fabrication Lab workspaces, and workers. Work health hazards requiring Health Surveillance may include but are not limited to: noise, hazardous chemicals, dangerous goods, fumes, dust, gases and pathogens.
The State Library acknowledges that it has obligations under current Queensland Work Health and Safety Regulation 2011 to undertake Health Surveillance if exposing workers (including contractors and volunteers) members and visitors to hazardous chemicals and processes which have the potential to result in disease or adverse health effects. Health monitoring is not an alternative to implementing control measures.
The Edge Fabrication Lab will ensure that Health Surveillance is carried out if:
- A worker is carrying out on-going work using, handling or storing hazardous chemicals and there is a significant risk to the worker’s health because of exposure to a designated hazardous chemical, as described in the current WHS Legislation;
- If it is uncertain, on reasonable grounds whether the exposure to the hazardous chemicals has resulted in exceeding the biological exposure standard;
The following tasks will form the framework to identify the need to conduct Health Surveillance and the process involved in the conduct and monitoring of Health Surveillance:
- Identification of situations where a worker may have on-going exposure to hazardous chemicals and/or hazardous operations that may have a negative impact on their health;
- Assessment of the extent of the risk associated with the work;
- Establishment of control measures using the hierarchy of controls;
- Creation of a process for monitoring the health of workers, as per the relevant current WHS Legislation and Australian Standards;
- Regular consultation with workers who are required to participate in Health Surveillance, or who work in situations where their health may be negatively affected by on-going work with hazardous chemicals and/or processes;
- Documented systems to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of the risk control measures.
8.4 Health Surveillance Procedure
- Responsibilities:
The Edge Fabrication Lab Management Representative is responsible for ensuring that there is a safe system in place for workers
The Edge Fabrication Lab Management Representative, WHSA and HSR is responsible to:
- Determine if and when health surveillance and monitoring is required;
- Consult with workers during all phases of health surveillance;
- Maintain accurate records including the Health Surveillance Record;
- Familiarity and understanding of this and any other procedures associated with health surveillance and monitoring;
- Liaison and coordinate with registered medical practitioners engaged by The Edge Fabrication Lab to perform health monitoring services;
- Provide information and training to workers as required.
Workers are responsible to:
- Cooperate with reasonable directions in respect of health surveillance and monitoring processes;
- Wear appropriate personal protective protection as required as per the relevant SOP’s and workspace procedures;
- Be familiar with, understand and follow this procedure.
- Procedure:
The Management Representative will:
- Inform workers and prospective workers about health surveillance requirements;
- Ensure health monitoring is carried out by or under the supervision of a registered medical practitioner with experience in health monitoring;
- Consult workers regarding the selection of the registered medical practitioner as required;
- Pay all expenses relating to health monitoring of The Edge Fabrication Lab workers;
- Provide information about a worker to the registered medical practitioner;
- Take all reasonable steps to obtain a report from the registered medical practitioner as soon as practicable after the health monitoring has been carried out;
- Provide a copy of the report to the worker and State Authority, accompanied by a written explanation of the meaning and implications, if the report contains adverse test result or recommendations to take remedial measures;
- Retain reports as confidential records as per the State Library document disposal schedule;
- Complete and maintain the Health Surveillance Record;
- Not disclose the report to anyone without the worker’s written consent unless required under the current WHS Legislation.
The personal information of individual workers, including medical reports and Health Surveillance, will remain confidential at all times between the relevant senior manager and the worker.
For worker exposure to noise, refer to the Hearing Protection and Audiometric Testing Procedure.
Section 9 INDUCTION and TRAINING
9.1 Training, Competency and Induction
Objective: To provide WHS induction and training to all workers and contractors to ensure they have the skills and competencies to work in a manner that is safe and without risks to health.
Scope: This covers all people engaged to undertake tasks at The Edge Fabrication Lab workspaces/locations including workers, independent contractors and volunteers.
The State Library is committed to providing training to all workers to ensure they have the skills and demonstrated competencies to work in a manner that is safe and without risks to health and safety.
Training is vital to assist workers to perform their work safely and will be provided to cover health and safety issues related to tasks, as well as training in the overall approach to health and safety taken by our organisation.
The State Library will also provide WHSMS induction for workers at any workspace where individual workers are assigned.
9.2 Training and Competency Assessment Procedure
- Responsibilities:
The Edge Fabrication Lab Management Representative is responsible for ensuring that:
- Provision of budget, resources and time allocation to enable workers to undergo training and competency assessment per the requirements of the legislation;
- There is a practical worker training and competency assessment procedure and system in place;
- Review of the Training and Competency Procedure as required.
The Management Representative is responsible for:
- Sourcing training and licensing service provision from qualified and suitable training service providers and the coordination of timetabling of training delivery for workers;
- Maintaining and reviewing the Training and Competency Procedure as required;
- Ensuring all workers complete training and competency assessments as needed;
- Informing and consulting with the WHSA regarding worker training and competency;
- Maintaining records required by legislation relating to worker training and competency, using the Worker Training, Competency and Induction Register for The Edge Fabrication Lab.
- Informing workers about the requirement to participate in and completion of training and competency assessment as per the needs of their position;
- Ensuring that all workers complete training and evaluation as being competent to perform their duties within the required timeframe;
- Give adequate allocation of time and resources for workers to complete training as required;
All workers are responsible for actively participating in and completing training and competency assessments (on-the-job, internal/external courses, formal qualifications, licenses) relevant to the performance of their position while working at The Edge Fabrication Lab.
- Procedure:
The Management Representative will:
- Conduct training needs analysis across the organisation;
- Develop formal training needs and competencies for position requirements at all levels, including management and designated first aiders;
- Record all completed training and competency assessments in the Worker Training, Competency and Induction Register as appropriate;
- Determine, assess and record the training and competency needs and levels of workers and contractors;
- Provide formal training and competency assessment plans for new and transferred workers and contractors;
- Use Registered Training Organisations (RTO) and appropriately accredited and approved courses/trainers;
- Ensure training is competency based;
- Utilise the First Aid Worker Register for workers assigned with first aider duties;
- Review effectiveness of training;
- Provide managers and supervisors with additional training to ensure that they are aware of their duties and responsibilities under The Edge Fabrication Lab WHSMS Manual and the current WHS Legislation.
Provide a refresher of Training or Re-Certification if it becomes evident that a worker is unfamiliar with aspects of their training or if they are determined, via assessment and consultation, to be no longer competent to perform their job tasks by the Management Representative.
Training will include:
- All health and safety policies and procedures for the organisation;
- Licenses and competencies to perform tasks;
- Specific hazards and risk controls;
- Consultation and communication arrangements;
- Incident reporting and corrective actions;
- Emergency response;
- First aid.
All managers and supervisors will be provided with additional training to ensure that they are aware of their responsibilities under the WHSMS Manual. This training includes legislative responsibilities for managers and supervisors, HSR training plus training in the principles of risk management.
9.3 Workspace Induction Procedure
- Responsibilities:
The Edge Fabrication Lab Management Representative is responsible for ensuring that:
- There is a Workspace Induction Procedure and system in place;
- All workers are trained and familiar with the Workspace Induction Procedure and complete their Workspace Induction as required by the procedure;
- Conduct a review of the Workspace Induction Procedure, and the Workspace Safety Rules as necessary.
The Management Representative is responsible for:
- Maintaining and reviewing the Workspace Induction Procedure as required;
- Ensuring all workers complete their Workspace Induction before commencement of work;
- Ensuring all workers are familiar with and understand the Workspace Safety Rules, and have easy access to the Workspace Safety Rules at each workspace;
- Maintaining worker induction records, including the Worker Training, Competency and Induction Register.
- Informing workers and others about the requirement to participate in and complete a Workspace Induction before commencement of work;
- Ensuring all workers are familiar with and understand the Workspace Safety Rules;
- Assisting all people complete their Workspace Induction.
All workers are responsible for actively participating in and completing the workspace induction and for following reasonable directions in respect of safety procedures.
- Procedure:
- Inform the inductee (new worker) that they are required to participate in and complete the induction;
- A nominated, responsible person will work through the induction, including the Workspace Safety Rules with the inductee, step by step, and provides that all the necessary workspace inspection and information during the induction;
- In consultation with the inductee, the responsible person will complete the Workspace Induction Checklist, as each part of the induction is completed;
- The Workspace Induction Checklist is given to the inductee to sign and provide this signed copy to:
- The inductee (the worker);
- The Human Resources Manager;
- Provide additional Workspace Induction if there are any changes to the work workspace that affect the health and safety of workers;
- Provide a refresher of the Workspace Induction if it becomes evident that the worker is unfamiliar with aspects of the induction or if they are determined to be deliberately non-compliant with workspace safety procedures by the appropriate manager;
- Employee/Worker Training, Competency and Induction Register entry is completed for each worker a record kept.
Term and Definitions
Act: An act is a law (legislation) passed and enacted by a state or territory parliament, also commonly known as an Act of Parliament. Acts are the principal pieces of law covering, in this case, health and safety in the workspace.
Code of Practice (COP): is a practical guide to achieving the standards of WHS required under current WHS Legislation. A COP applies to anyone who has a duty of care in the circumstances described in the code. Mostly, following an approved COP would achieve compliance with the health and safety duties in the current WHS Act, with the subject matter of the code. Approved COP's are admissible in court proceedings under the current WHS Legislation. Attaining compliance with the current WHS Legislation may also be achieved by following another method, such as a technical or an industry standard if it provides an equivalent or higher standard of WHS than the code.
Contractor: A contractor is any person (other than a The Edge Fabrication Lab worker) or a company performing work for, or on behalf of The Edge Fabrication Lab.
Controlled document or record: Any document for which distribution and status are to be kept current by the issuer to ensure that authorised holders or users have available the most up to date version.
Corrective Action: A corrective action is an action, which is taken to eliminate the cause of an identified compliance breach or a hazard.
Dangerous Goods: Dangerous Goods within the meaning of the relevant State or Territory Dangerous Goods Act and the Regulations under that Act.
Decibel: is the unit for measuring sound levels.
Emergency service:
- Rural Fire Authority; or
- Fire Brigade (State); or
- Ambulance Service; or
- State Emergency Service; or
- Police (State).
FOA: First Aid officer.
Hazard: A hazard is a source or a situation with a potential for harm regarding human injury or illness, damage to property, damage to the environment, or a combination of these.
Hazardous Chemical: A chemical that meets the criteria for classification as being hazardous according to the current WHS Regulations. A substance is any natural or artificial substance, whether in the form of a solid, liquid, gas or vapour.
Hierarchy of Control: A hierarchical structure of actions that can be used to control risk, listed in order of effectiveness.
HSR: Health & safety representative
Incident: An incident is any unplanned event resulting in, or having a potential to result in injury, ill health, damage or loss.
Lost Time Injury (LTI): An injury or illness that occurs in the workspace as a result of an activity, or exposure to a hazard and results in at least one full day absence from work.
LOTO: Lock out, tag out.
LTI Average Days Lost Rate: The average days lost per accounting period
LTI Incident Rate: The rate of LTI injuries or illnesses expressed as per 100 workers.
Manifest: A manifest is different from a Substance Register. A manifest is a written summary of specific types of dangerous goods that are used, handled or stored at a workspace. Its purpose is to provide the emergency services organisations with detailed information they require and includes workspace plans and emergency contact details.
Management Representative: Is the appointed representative for the PCBU to establish, implement and maintain the WHSMS in accordance with regulations, standards and guidance.
Members: A member of the public with a current State Library of Queensland account.
PCBU: “Person who Conducts a Business or Undertaking'”. The definition of a PCBU is similar to an employer; however, it is termed PCBU to recognise other relevant relationships (such as someone who commissions work, or a landlord) under the current WHS Legislation.
Placard: A sign or notice that is displayed in a prominent place, next to a container or storage area for Dangerous Goods at a workspace. It contains information about the Dangerous Goods in containers or a storage area. Placards on trucks/vehicles transporting Dangerous Goods.
Plant: includes -
- Any machinery, equipment, appliance, implement and tool; and
- Any component of any of those things; and
- Anything fitted, connected or related to any of those things.
PPE: Personal protection equipment
RA: Risk Assessment
Regulations: Regulations are the law created under the authority of an Act. Regulations are subordinate to an Act and prescribe in detail the requirements needed to support the duties established in the Act.
Risk: Risk is a combination of the likelihood and consequences of any injury or harm occurring due to specified hazards.
Safety Data Sheet (SDS): Information containing data regarding the properties and effects of a particular chemical provided by the manufacturer, supplier or importer of the hazardous chemical/dangerous good. SDS must be current – within five years of the issue date and meet specific legislated format requirements.
Self-employed person: A person, other than a PCBU, who works for gain or reward other than under a contract of employment or training.
SOP: Safe operating procedure.
SWMS: Safe work method statement.
Visitors: Any member of the public visiting the State Library of Queensland in a recreational or professional capacity.
Volunteer: A person who is acting on a voluntary basis (irrespective of whether the person receives out-of-pocket expenses).
WHSA: Work, Health & Safety Advisor. The role of the WHSA is to assist the Principal, Managers and/or management team by providing advice on health and safety at the workplace.
WHS Documents: Include, but not limited to policies, procedures, guidelines, plans, agreements, forms, checklists, templates, risk assessments and safe work procedures.
WHS Records: Include, but not limited to audit reports, workspace inspections, risk assessments, safe work procedures, training plans and registers, WHS meeting minutes, emergency evacuation reports, health monitoring reports, document control registers, inspection testing and monitoring reports and corrective action registers.
WHSMS: Work, Health & Safety management system.
Worker: is a person, who carries out work in any capacity for a PCBU, including work as:
- A worker, or
- A contractor or subcontractor, or
- A worker of a contractor or subcontractor, or
- A worker of a labour-hire company who has been assigned to work in the person's business or undertaking, or
- An out-worker, or
- An apprentice or trainee, or
- A student gaining work experience, or
- A volunteer, or
- A person of a prescribed class.
Workspace: means a place where work is carried out for business or undertaking and includes any situation where a worker goes or is likely to be while at work. A workspace includes:
- A vehicle, vessel, aircraft or other mobile structure; and
- Any waters and any installations on land, on the bed of any waters or floating on any waters.
References
Australian Standards
- Standards Australia 2001, – Occupational health and safety management systems - Specification with guidance for use, AS/NZS 4801: 2001
Queensland State Legalisation
Queensland Environmental Legislation
Australian Code of Practice
Queensland Code of Practice
WHS Regulators
Worksafe Queensland
(Workplace Health and Safety, Electrical Safety Office, Workers' Compensation Regulator)
https://www.worksafe.qld.gov.au
Australian Government (Comcare) –
https://www.comcare.gov.au/home
Advisory Body
Safe Work Australia –
https://www.safeworkaustralia.gov.au/
Further information on Legislation and codes of practice can be found here:
Queensland OHS Legislation –
Queensland Environmental Legislation –
https://www.ehp.qld.gov.au/management/env-policy-legislation/
Queensland OHS Codes of Practice –
Safe Work Australia Codes of Practice –
https://www.safeworkaustralia.gov.au/resources_publications/model-codes-of-practice
Australian Standard AS/NZS 4801: 2001 –
https://www.comcare.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0005/166694/04734_RO_WHSMS_snapshot_v4.pdf